3.1.3 Vector Algebra FunctionsModeler2D vector algebra functions perform many common vector algebra operations such as cross and dot products of vectors. These functions can be used to build more complicated functions that are not provided by Modeler2D. The output functions take point, vector, and axis objects as arguments, identical in structure to the geometry objects used when building constraint objects. When local point numbers are used, the local coordinates are taken from the current body objects, as specified with SetBodies.
Each of the vector algebra functions are demonstrated in the context of the quick-return mechanism model defined at the beginning of this section. Vector algebra functions. The Direction function is used to convert Modeler2D vector objects into 2D vectors in global coordinates. Note that Mech's definition of Direction does not interfere with its use as a built-in Mathematica symbol. Here is the direction vector of the connecting rod.
Out[33]= | 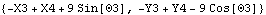 |
Now get a numerical result.
Out[34]= | 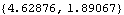 |
Several Modeler2D output functions are textbook vector algebra functions that are capable of dealing with normal 2D vectors or Modeler2D line objects interchangeably. Magnitude can return the length of the line from one end of the connecting rod to the other.
Out[35]= | 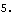 |
Magnitude also works with simple vectors.
Out[36]= | 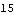 |
Unit also works with vectors or line objects.
Out[37]= | 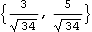 |
The cross product of two vectors in 2D space is a scalar.
Out[38]= | 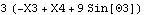 |
Now get a numerical result.
Out[39]= | 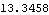 |
Here is a 2D rotation matrix that will rotate a vector on the slider into global coordinates.
Out[40]= | 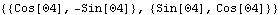 |
The global coordinates of a point specified in a local reference frame are equal to the coordinates of the origin of the reference frame plus the local coordinates of the point, rotated into the global reference frame. Here is a calculation of the global coordinates of the local point {3, 8} on the slider.
Out[41]= | 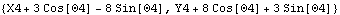 |
The Location function performs effectively the same calculation, directly.
Out[42]= | 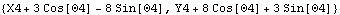 |
Now get a numerical result.
Out[43]= | 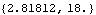 |
The PointToLocal function converts the global point back to local coordinates.
Out[44]= | 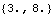 |
Two constant matrices that are commonly used in 2D vector algebra are also defined by Modeler2D. Constant utilities. Coordinate ConversionsPolarToXY and XYToPolar are two conversion functions that do not accept Modeler2D geometry objects as arguments. These functions only accept 2D vectors of the form {x, y}. Coordinate conversions. This converts a polar coordinate pair to Cartesian coordinates.
Out[45]= | 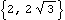 |
This converts it back.
Out[46]= | 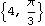 |
This converts a 2D vector to polar coordinates.
Out[47]= | 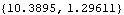 |
|