AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[data,hspec]
estimates the absolute correlation function at lags hspec from data.
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,hspec]
represents the absolute correlation function at lags hspec for the random process proc.
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,s,t]
represents the absolute correlation function at times s and t for the random process proc.


AbsoluteCorrelationFunction
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[data,hspec]
estimates the absolute correlation function at lags hspec from data.
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,hspec]
represents the absolute correlation function at lags hspec for the random process proc.
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,s,t]
represents the absolute correlation function at times s and t for the random process proc.
Details

- AbsoluteCorrelationFunction is also known as the autocorrelation function.
- The following specifications can be given for hspec:
-
τ at time or lag τ {τmax} unit spaced from 0 to τmax {τmin,τmax} unit spaced from τmin to τmax {τmin,τmax,dτ} from τmin to τmax in steps of dτ {{τ1,τ2,…}} use explicit {τ1,τ2,…} - AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[{x1,…,xn},h] is equivalent to
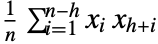 .
. - When data is TemporalData containing an ensemble of paths, the output represents the average across all paths.
- AbsoluteCorrelationFunction for a process proc with value x[t] at time t is given by:
-
Expectation[x[s] x[t]] for a scalar-valued process Expectation[x[s]⊗x[t]] for a vector-valued process - The symbol ⊗ represents KroneckerProduct.
- AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,h] is defined only if proc is a weakly stationary process and is equivalent to AbsoluteCorrelationFunction[proc,h,0].
- The process proc can be any random process such as ARMAProcess and WienerProcess.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (13)
Empirical Estimates (7)
Estimate the absolute correlation function for some data at lag 5:
Obtain empirical estimates of the correlation function up to lag 9:
Compute the absolute correlation function for lags 1 to 9 in steps of 2:
Compute the absolute correlation function for a time series:
The absolute correlation function of a time series for multiple lags is given as a time series:
Estimate the absolute correlation function for an ensemble of paths:
Compare empirical and theoretical absolute correlation functions:
Random Processes (6)
The absolute correlation function for a weakly stationary discrete-time process:
The absolute correlation function only depends on the antidiagonal ![]() :
:
The absolute correlation function for a weakly stationary continuous-time process:
The absolute correlation function only depends on the antidiagonal ![]() :
:
The absolute correlation function for a non-weakly stationary discrete-time process:
The absolute correlation function depends on both time arguments:
The absolute correlation function for a non-weakly stationary continuous-time process:
The absolute correlation function depends on both time arguments:
The correlation function for some time series processes:
Absolute cross-correlation plots for a vector ARProcess:
Applications (2)
Determine whether the following data is best modeled with an MAProcess or an ARProcess:
It is difficult to determine the underlying process from sample paths:
The absolute correlation function of the data decays slowly:
ARProcess is clearly a better candidate model than MAProcess:
Use the absolute correlation function to determine if a process is mean ergodic:
The process is weakly stationary:
Calculate the absolute correlation function:
Find the value of the strip integral:
Check if the limit of the integral is 0 to conclude mean ergodicity:
Properties & Relations (13)
Sample absolute correlation function is a biased estimator for the process absolute correlation function:
Calculate the sample absolute correlation function:
Absolute correlation function for the process:
Absolute correlation function for a list can be calculated using AbsoluteCorrelation:
Calculate absolute correlation function for the data:
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction is the off-diagonal entry in the absolute correlation matrix:
Sample absolute correlation function at lag 0 estimates the second Moment:
Sample absolute correlation function is related to CovarianceFunction:
Sample absolute correlation function is related to CorrelationFunction:
Compare to the sample correlation function:
Use Expectation to calculate the absolute correlation function:
The absolute correlation function ![]() is related to the Moment function:
is related to the Moment function:
Verify equality ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the
is the ![]()
![]() moment function:
moment function:
The absolute correlation function ![]() is related to the CovarianceFunction
is related to the CovarianceFunction ![]() :
:
Verify equality ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the mean function:
is the mean function:
The absolute correlation function equals CovarianceFunction when the mean of the process is zero:
The absolute correlation function is invariant for ToInvertibleTimeSeries:
The absolute correlation function is not invariant to centralizing:
Compare absolute correlation functions:
PowerSpectralDensity is a transform of the absolute correlation function for mean zero processes:
Use FourierSequenceTransform with appropriate parameters:
Possible Issues (1)
AbsoluteCorrelationFunction output may contain DifferenceRoot:
Use FunctionExpand to recover explicit powers:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), AbsoluteCorrelationFunction, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsoluteCorrelationFunction.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "AbsoluteCorrelationFunction." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsoluteCorrelationFunction.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). AbsoluteCorrelationFunction. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsoluteCorrelationFunction.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_absolutecorrelationfunction, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AbsoluteCorrelationFunction}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsoluteCorrelationFunction.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_absolutecorrelationfunction, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AbsoluteCorrelationFunction}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsoluteCorrelationFunction.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}