represents a Bartlett window function of x.


BartlettWindow
represents a Bartlett window function of x.
Details

- BartlettWindow, also known as the triangular window, is a window function typically used for antialiasing and resampling.
- Window functions are used in applications where data is processed in short segments and have a smoothing effect by gradually tapering data values to zero at the ends of each segment.
- BartlettWindow[x] is equal to
![ 1-2 x 0<=x<=1/2; 1+2 x -1/2<=x<0; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>1/2; 1-2 x 0<=x<=1/2; 1+2 x -1/2<=x<0; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>1/2;](Files/BartlettWindow.en/2.png) .
. - BartlettWindow automatically threads over lists.
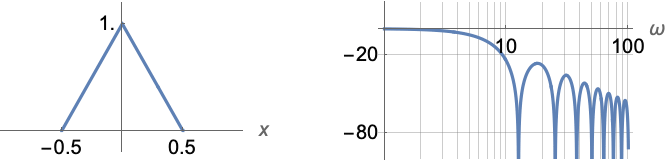
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (4)
Applications (4)
Create a moving average filter of length 11:
Taper the filter using a Bartlett window:
Log-magnitude plot of the power spectra of the two filters:
Filter a white noise signal using the Bartlett window method:
Use a window specification to calculate sample PowerSpectralDensity:
Compare to spectral density calculated without a windowing function:
The plot shows that window smooths the spectral density:
Compare to the theoretical spectral density of the process:
Properties & Relations (6)
BartlettWindow is equivalent to a compressed UnitTriangle:
The area under the Bartlett window:
Normalize to create a window with unit area:
Fourier transform of the Bartlett window:
Power spectrum of the Bartlett window:
Discrete Bartlett window of length 15:
Normalize so the coefficients add up to 1:
Discrete-time Fourier transform of a normalized discrete Bartlett window of length 15:
Power spectra of the Bartlett and rectangular window sequences:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), BartlettWindow, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BartlettWindow.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "BartlettWindow." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BartlettWindow.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). BartlettWindow. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BartlettWindow.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_bartlettwindow, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BartlettWindow}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BartlettWindow.html}", note=[Accessed: 19-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_bartlettwindow, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BartlettWindow}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BartlettWindow.html}, note=[Accessed: 19-February-2026]}