x+y+z
represents a sum of terms.


Plus 
x+y+z
represents a sum of terms.
Details

- Plus has attributes Flat, Orderless, and OneIdentity.
- The default value for arguments of Plus, as used in x_. patterns, is 0. »
- Plus[] is taken to be 0.
- Plus[x] is x.
- x+0 evaluates to x, but x+0.0 is left unchanged.
- In mixed fractions such as 1
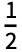 , the implicit addition can be entered as 1
, the implicit addition can be entered as 1  +
+
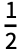 or 1 \[ImplicitPlus]
or 1 \[ImplicitPlus] 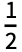 . This evaluates to 1+
. This evaluates to 1+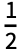 , but implicit addition is an operator with much higher precedence than +.
, but implicit addition is an operator with much higher precedence than +. - Unlike other functions, Plus applies built‐in rules before user‐defined ones. As a result, it is not possible to make definitions such as 2+2=5.
- Plus can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Background & Context
- Plus is a function that does addition (summation) of expressions. The expression Plus[a,b,c,…] is commonly represented using the shorthand syntax a+b+c+…. Special cases include Plus[], which is taken to be 0, and Plus[x], which is taken to be x.
- Plus sorts its arguments and collapses any terms of the same type. Plus also threads element-wise over lists.
- To perform summation at a particular level of a list or to apply compensative summation to reduce numerical error for inexact summands, the function Total can be used. Accumulate gives a list of the successive accumulated totals of elements in a list. AddTo, Increment, and PreIncrement can be used to increase the value of a given variable. Minus gives the arithmetic negation of an expression, and Subtract gives the difference of two numbers.
- Summation of a function over a range or list of arguments is done using the function Sum.
Examples
open all close allScope (6)
If any number is approximate, the whole result will be as follows:
Complex numbers add their components:
Plus threads element-wise over lists:
Create mixed fractions by typing a whole number, ![]() +
+![]() , and a fraction:
, and a fraction:
Plus can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Properties & Relations (10)
Plus sorts its arguments:
Display terms in a sum in a traditional order:
Display a sum without evaluation:
Display the FullForm of a sum:
Pattern matching works with Plus:
Distribute a function over Plus:
Distribute Plus through a head:
Starting from f+g, use Comap to distribute the sum across an argument:
Accumulate makes a cumulative sum:
Related Guides
-
▪
- Arithmetic Functions ▪
- GPU Computing ▪
- Image Processing & Analysis ▪
- Matrix Operations ▪
- Wolfram Language Syntax ▪
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA ▪
- Matrices and Linear Algebra ▪
- Operations on Vectors ▪
- Handling Arrays of Data ▪
- GPU Computing with Apple ▪
- Mathematical Functions ▪
- Audio Editing ▪
- Associations
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 1996 (3.0) ▪ 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Plus, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Plus.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Plus." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Plus.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Plus. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Plus.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_plus, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Plus}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Plus.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_plus, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Plus}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Plus.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}