- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Math & Counting Operations on Lists
- Arithmetic Functions
- Computation with Structured Datasets
- List Manipulation
- Operations on Vectors
- GPU Computing
- Numerical Data
- Tensors
- Discrete & Integer Data
- Matrices and Linear Algebra
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA
- GPU Computing with Apple
- Mathematical Functions
- Tabular Transformation
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
- Tech Notes
-
- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Math & Counting Operations on Lists
- Arithmetic Functions
- Computation with Structured Datasets
- List Manipulation
- Operations on Vectors
- GPU Computing
- Numerical Data
- Tensors
- Discrete & Integer Data
- Matrices and Linear Algebra
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA
- GPU Computing with Apple
- Mathematical Functions
- Tabular Transformation
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
- Tech Notes


Total
Details and Options
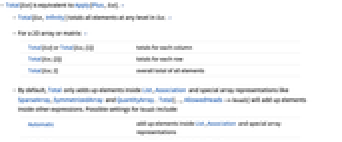
- Total[list] is equivalent to Apply[Plus,list]. »
- Total[list,Infinity] totals all elements at any level in list. »
- For a 2D array or matrix: »
-
Total[list] or Total[list,{1}] totals for each column Total[list,{2}] totals for each row Total[list,2] overall total of all elements - By default, Total only adds up elements inside List, Association and special array representations like SparseArray, SymmetrizedArray and QuantityArray. Total[…,AllowedHeads->heads] will add up elements inside other expressions. Possible settings for heads include:
-
Automatic add up elements inside List, Association and special array representations Inherited add up elements inside Head[expr] All add up elements inside any normal expression Association add up the values in Association List adds up elements in lists h add up elements inside h {h1,…} add up elements inside any of h1,… - Total[list,Method->"CompensatedSummation"] uses compensated summation to reduce numerical error in the result. »
- Total works with SparseArray objects. »
Examples
open all close allScope (6)
Use exact arithmetic to total the values:
Use 47-digit precision arithmetic:
Total the columns of a matrix:
Total by adding parts in the first dimension:
Total in the last dimension only:
Total in the last two dimensions:
Total all but the last dimension:
Total the last dimension in a ragged array:
You cannot total in the first dimension because the lists have incompatible lengths:
Options (2)
Method (1)
Use Method->"CompensatedSummation" to reduce accumulated errors in a sum:
Without compensated summation, small errors may accumulate with each term:
AllowedHeads (1)
Total[expr,AllowedHeads->Inherited] works with any head:
Applications (3)
Form a polynomial from monomials:
Show that the trace of a matrix is equal to the total of its eigenvalues:
Search for "perfect" numbers equal to the sum of their divisors:
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
-
▪
- Math & Counting Operations on Lists ▪
- Arithmetic Functions ▪
- Computation with Structured Datasets ▪
- List Manipulation ▪
- Operations on Vectors ▪
- GPU Computing ▪
- Numerical Data ▪
- Tensors ▪
- Discrete & Integer Data ▪
- Matrices and Linear Algebra ▪
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA ▪
- GPU Computing with Apple ▪
- Mathematical Functions ▪
- Tabular Transformation ▪
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
Related Links
- An Elementary Introduction to the Wolfram Language : Operations on Lists
- An Elementary Introduction to the Wolfram Language : Associations
- An Elementary Introduction to the Wolfram Language : Assigning Names to Things
- An Elementary Introduction to the Wolfram Language : Datasets
- An Elementary Introduction to the Wolfram Language : Writing Good Code
History
Introduced in 2003 (5.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2019 (12.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2003), Total, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Total.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2003. "Total." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Total.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2003). Total. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Total.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_total, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Total}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Total.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-January-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_total, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Total}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Total.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-January-2026]}