TreeLevel
TreeLevel[tree,levelspec]
gives a list of all subtrees of tree on levels specified by levelspec.
TreeLevel[tree,levelspecelem]
gives a list of the element elem of subtrees on levels specified by levelspec.
Details and Options

- TreeLevel lists the subtrees on any range of levels in a Tree object. The list of subtrees can be given in many different orders, including depth-first and breadth-first traversals.
- TreeLevel[tree,levelspec] gives a list of the subtrees on the given levels. This can also be expressed as TreeLevel[tree,levelspec"Subtree"].
- TreeLevel[tree,levelspec"Data"] gives a list of the data on the given levels.
- TreeLevel uses standard level specifications:
-
n levels 1 through n All levels 0 through Infinity Infinity levels 1 through Infinity {n} level n only {n1,n2} levels n1 through n2 "Leaves" level -1 only "NonLeaves" levels 0 through -2 - A positive level n+1 consists of all subtrees of tree that are children of subtrees on level n.
- Level 0 corresponds to the root of the tree.
- Level -1 corresponds to the leaves.
- A negative level -(n+1) consists of all subtrees whose children are on levels -1, -2, …, -n, with highest level -n.
- TreeLevel traverses subtrees in a left-to-right, depth-first order, with children visited before their parents.
- TreeLevel[…,TreeTraversalOrderorder] allows visiting subtrees in different orders, such as depth-first and breadth-first traversals.
- TreeLevel[levelspec][tree] is equivalent to TreeLevel[tree,levelspec].
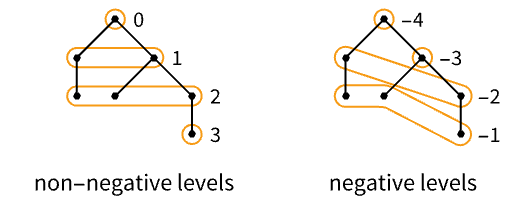
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Extract the subtrees on the second level:
Extract the data on a range of levels:
Use the operator form of TreeLevel:
Scope (8)
Level Specifications (7)
Extract the subtrees on all levels:
Extract the subtrees on levels 1, 2 and 3:
Extract the subtrees only on level 3:
Extract all levels, starting at level 1:
Positive and negative levels can be mixed:
Use TreeLevel as an operator form in a tree position specification:
Options (3)
TreeTraversalOrder (3)
By default, subtrees are listed in a depth-first order, with parents visited after their children:
Specify a top-down, right-to-left variant:
List subtrees in a breadth-first order, with nodes on the same level from the root visited before the nodes on the next level:
List subtrees in a leaves-first order, with nodes on the same level from the leaves visited before the nodes on the next level:
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (4)
TreeLevel[tree,levelspec] is equivalent to TreeChildren@TreeExtract[tree,TreeLevel[levelspec]]:
Level[expr,levelspec] is equivalent to TreeLevel[ExpressionTree[expr,"Subexpressions"],levelspec"Data"]:
Level[expr,levelspec,HeadsTrue] is equivalent to TreeLevel[ExpressionTree[expr,"Subexpressions",HeadsTrue],levelspec"Data"] for positive levels:
TreeLeaves gives the subtrees at level -1:
Possible Issues (1)
TreeLevel by default starts at level 1, so does not extract the whole tree:
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), TreeLevel, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeLevel.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "TreeLevel." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeLevel.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). TreeLevel. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeLevel.html