represents the sporadic simple Fischer group ![]() .
.


FischerGroupFi24Prime
represents the sporadic simple Fischer group ![]() .
.
Background & Context
- FischerGroupFi24Prime[] represents the Fischer group
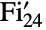 , which is a group of order
, which is a group of order ![TemplateBox[{2, 21}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{3, 16}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{5, 2}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{7, 3}, Superscript].11.13.17.23.29 TemplateBox[{2, 21}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{3, 16}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{5, 2}, Superscript].TemplateBox[{7, 3}, Superscript].11.13.17.23.29](Files/FischerGroupFi24Prime.en/3.png) . It is one of the 26 sporadic simple groups of finite order.
. It is one of the 26 sporadic simple groups of finite order. - The Fischer group
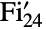 is the third largest of the sporadic finite simple groups. It was introduced by Bernd Fischer in the 1970s and first defined in terms of a rank-3 action on the graph of
is the third largest of the sporadic finite simple groups. It was introduced by Bernd Fischer in the 1970s and first defined in terms of a rank-3 action on the graph of 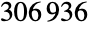 vertices corresponding to its 3-transpositions. In addition to its default permutation representation, which has as its point stabilizer the Fischer group
vertices corresponding to its 3-transpositions. In addition to its default permutation representation, which has as its point stabilizer the Fischer group 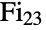 , FischerGroupFi24Prime has an irreducible representation of dimension 781 over the field
, FischerGroupFi24Prime has an irreducible representation of dimension 781 over the field 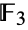 with three elements and has a finite cover that centralizes an element of order three in the monster group. Along with the other sporadic simple groups, the Fischer groups played a foundational role in the monumental (and complete) classification of finite simple groups.
with three elements and has a finite cover that centralizes an element of order three in the monster group. Along with the other sporadic simple groups, the Fischer groups played a foundational role in the monumental (and complete) classification of finite simple groups. - The usual group theoretic functions may be applied to FischerGroupFi24Prime[], including GroupOrder, GroupGenerators, GroupElements and so on. However, while FischerGroupFi24Prime[] is a permutation group, due its large order, an explicit permutation representation is impractical for direct implementation. As a result, a number of such group theoretic functions may return unevaluated when applied to it. A number of precomputed properties of the Fischer group
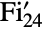 are available via FiniteGroupData[{"Fisher",24},"prop"].
are available via FiniteGroupData[{"Fisher",24},"prop"]. - FischerGroupFi24Prime is related to a number of other symbols. FischerGroupFi24Prime is one of the eight groups (along with FischerGroupFi22, FischerGroupFi23, HeldGroupHe, HaradaNortonGroupHN, ThompsonGroupTh, BabyMonsterGroupB and MonsterGroupM) collectively referred to as the "third generation" of sporadic finite simple groups. It is also one of 20 so-called "happy" sporadic groups, which all appear as a subquotient of the monster group.
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), FischerGroupFi24Prime, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FischerGroupFi24Prime.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "FischerGroupFi24Prime." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FischerGroupFi24Prime.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). FischerGroupFi24Prime. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FischerGroupFi24Prime.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_fischergroupfi24prime, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FischerGroupFi24Prime}", year="2010", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FischerGroupFi24Prime.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_fischergroupfi24prime, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FischerGroupFi24Prime}, year={2010}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FischerGroupFi24Prime.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}