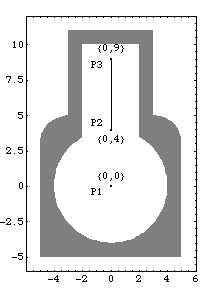
1.2.2 2D BodiesGroundThe local coordinate system of the ground body originates at the rotational center of the crankshaft. Three points are used on the ground body.
P1 is a point at the global origin that is the rotational axis of the crankshaft.
P2 and P3 are two points that define the vertical line upon which the piston translates.Here is a graphic of the ground body.
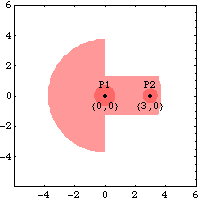
CrankshaftThe local coordinate system of the crankshaft originates at its rotational center. Two points are used on the crankshaft.
P1 is a point at the local origin that is the rotational axis of the crankshaft.
P2 is a point on the local x axis that is the attachment point of the connecting rod.Here is a graphic of the crankshaft.
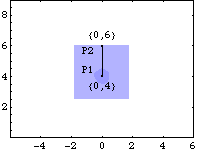
PistonThe local coordinate system of the piston originates four units below the attachment point of the connecting rod. Thus, when the mechanism is in its initial configuration, the local origin of the piston is coincident with the global origin. Two points are used on the piston.
P1 is the attachment point of the connecting rod.
P2 is used with P1 to define the vertical translation line of the piston.Here is a graphic of the piston.
|