9.5.2 Sensitivity to Parameter VariationsThe quick-return model contains three undefined parameters: crankarm, drivex, and drivey. We wish to find the sensitivity of the location of each body in the mechanism to small changes in these parameters, about some operating point. The sensitivities are not constant, they change as the mechanism moves through a complete cycle. Thus, the maximum sensitivity at any point in a cycle is of interest. The values of the parameters are set and the body locations are found at the initial operating point.
Out[10]= | 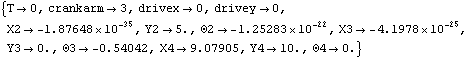 |
The sensitivity functions. First, the sensitivity to variations in the crankarm parameter are found. This builds the SensitivitySystem object.
Out[11]= | 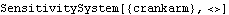 |
This solves the SensitivitySystem object.
Out[12]= | 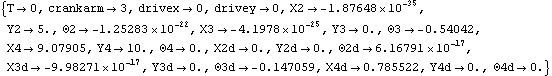 |
The solution returned by SolveSensitivity is identical in form to the solution returned by SolveMech[time, Solution -> Velocity]. The difference is that the velocity terms X2d,  3d, and so on, do not represent dX2/dT and d 3d, and so on, do not represent dX2/dT and d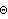 3/dT; they represent dX2/dcrankarm and d 3/dT; they represent dX2/dcrankarm and d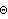 3/dcrankarm. Because the results from SolveSensitivity are returned in this form, it is possible to use any of the MechanicalSystems' output functions, differentiated once, to find the sensitivity of more complicated quantities to changes in the parameter. 3/dcrankarm. Because the results from SolveSensitivity are returned in this form, it is possible to use any of the MechanicalSystems' output functions, differentiated once, to find the sensitivity of more complicated quantities to changes in the parameter. Here is the sensitivity of the distance from the crank center to the slider origin to changes in crankarm.
Out[13]= | 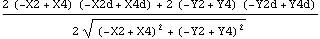 |
Out[14]= | 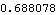 |
|