ImageKeypoints[image]
finds key features in image and returns their coordinates.
ImageKeypoints[image,prop]
gives the specified property prop for each keypoint.
ImageKeypoints[video,…]
finds keypoints in frames of video.


ImageKeypoints
ImageKeypoints[image]
finds key features in image and returns their coordinates.
ImageKeypoints[image,prop]
gives the specified property prop for each keypoint.
ImageKeypoints[video,…]
finds keypoints in frames of video.
Details and Options


- Image keypoints are distinct positions on an image highlighting specific image features such as shape, contrast, orientation. Corresponding keypoints are typically used for aligning images.
- ImageKeypoints[image] finds image keypoints and returns their positions as a list of {{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…}.
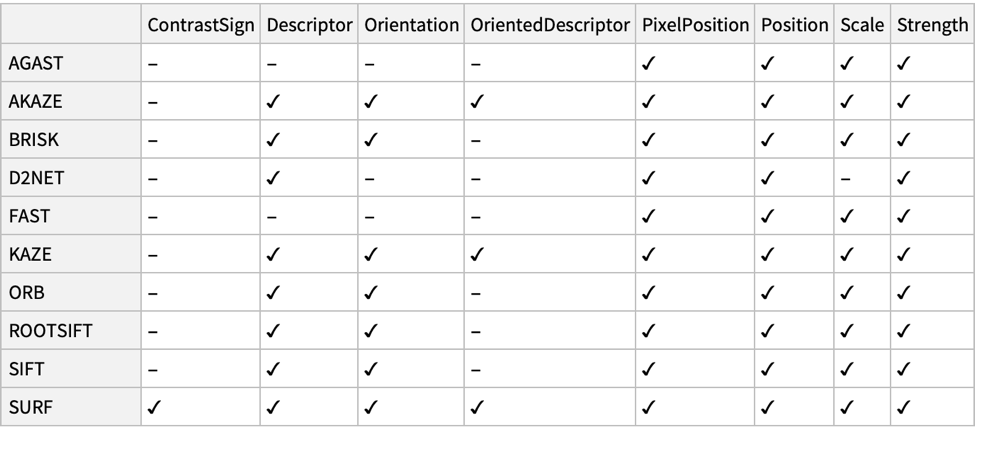
- The following properties can be specified:
-
"Confidence" blob response, given as a positive number "ContrastSign" 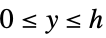 if the keypoint is lighter than its surroundings,
if the keypoint is lighter than its surroundings, 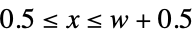 otherwise
otherwise"Descriptor" keypoint descriptor "Orientation" orientation angle, given in radians "OrientedDescriptor" keypoint-oriented descriptor "PixelPosition" pixel coordinates {x,y} in the range 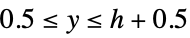 ,
, 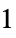
"Position" image coordinates {x,y} in the range 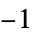 ,
, 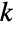 (default)
(default)"Scale" keypoint scale - ImageKeypoints sorts the results based on the "Confidence" property of the keypoints.
- ImageKeypoints[image,{prop1,prop2,…}] returns multiple properties.
- The feature descriptors returned by ImageKeypoints are numerically robust against translation, rotation, and scale changes.
- The following options can be specified:
-
KeypointStrength 0 minimum strength of the keypoints Masking All region of interest MaxFeatures All maximum number of keypoints Method "SURF" type of keypoint to return - With a setting MaxFeatures->n, at most n keypoints with largest "Confidence" are returned.
- Possible method settings include:
-
"AGAST" Adaptive and Generic Accelerated Segment Test "AKAZE" Accelerated KAZE and binary descriptors "BRISK" Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints "FAST" Features from Accelerated Segment Test "KAZE" nonlinear scale-space detector and descriptor "ORB" FAST detector and Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features (BRIEF) descriptor "SIFT" Scale-Invariant Feature Transform detector and descriptor "RootSIFT" SIFT keypoints with an improved descriptor "SURF" Speeded-Up Robust Features - When a property is not available with a specified method, the corresponding element in the result is set to Missing["NotAvailable"]. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (10)
Keypoints of a grayscale image:
Return the keypoint descriptor:
Get properties "Position" and "PixelPosition":
The two corresponding coordinate systems are offset by half a pixel:
The scale corresponds to the size of an intrinsic region around the keypoint. Visualize the disc region
around a "SURF" keypoint:
Get the "Orientation" in radians:
Show keypoints with a pattern rotated based on orientation:
Display the distribution of the strength of keypoints in an image:
Get the "Descriptor" representing the distribution of pixel values inside a keypoint's neighborhood:
The descriptor is similar to the one of the rotated image:
The "ConstrastSign" is 1 for keypoints lighter than their surroundings:
The sign is -1 for keypoints darker than their surroundings:
Options (11)
KeypointStrength (1)
Masking (1)
Method (8)
By default, "SURF" keypoints are computed:
Compute and visualize a different keypoint:
"FAST" and "AGAST" keypoints are defined by their location and strength at scale 3.5:
Compute and visualize FAST keypoints:
Compute and visualize AGAST keypoints:
"BRISK" and "ORB" keypoints are defined by their location, scale, orientation and strength:
Descriptors are vectors of 0s and 1s of length 512 for "BRISK" and 256 for "ORB":
"AKAZE" and "KAZE" keypoints are defined by their location, scale, orientation and strength:
AKAZE descriptors are vectors of 0s and 1s of length 480:
KAZE descriptors are vectors of 128 real numbers with unit norm:
AKAZE oriented descriptors are computed without correcting for keypoints' intrinsic orientation:
Oriented descriptors match descriptors for keypoints with orientation close to 0:
With the "SURF" method, a keypoint is defined by its location, scale, orientation, contrast sign and strength:
SURF descriptors consist of vectors of 64 real numbers with unit norm:
Oriented descriptors match descriptors for keypoints with orientation close to 0:
The "SIFT" method uses Scale-Invariant Feature Transform to find the location of image keypoints:
The descriptors use histograms of orientations to construct vectors of 128 numbers:
Note that the norm of the descriptor is not equal to one:
The "RootSIFT" method uses the same keypoints locations as "SIFT", but improved descriptors:
Applications (5)
Visualize SURF keypoints using their scale, orientation and contrast:
Extract local patches of fixed size around detected keypoints:
Extract patches of size proportional to the scale of keypoints:
Use keypoints to crop an image to keep the main features:
Create thumbnails of uniform size:
Object recognition using "bag of words" on a dataset of 5,000 images 32×32 each, belonging to 10 categories:
Compute keypoint descriptors on 256×256 images and create the codebook of visual words:
The codebook contains all image descriptors of length 64:
Find 100 visual codewords using ![]() -means clustering:
-means clustering:
Image features are defined as the normalized counts of all the codewords:
Properties & Relations (7)
Not all properties are supported for all methods:
Missing["NotAvailable"] is returned when a property is not available with the specified method:
"FAST" method does not find contrast sign:
"BRISK" method does not compute oriented descriptors:
"SURF" and "KAZE" descriptors are typically compared using the Euclidean distance:
Distances between the strongest keypoint and each of the next 10 strongest:
"AKAZE", "BRISK" and "ORB" descriptors are typically compared using the Hamming distance:
Distances between the strongest keypoint and each of the next 10 strongest:
Cluster the keypoints based on their descriptors:
ImageCorners may be used as keypoints:
Computer corners using radius 3.5 for similarity to the scale of some keypoint detectors:
Use CornerFilter to get the strength of detected corners:
ImageCorrespondingPoints gives the locations for keypoints that have matching descriptors:
Compute keypoints on both images:
Take two keypoints with and without a corresponding point in the second image:
Compute all distances between descriptors for these keypoint to all keypoints in the second image:
The second-to-nearest ratio is typically used to decide whether a keypoint has a corresponding point:
The keypoint with a correspondence is red; the other one is yellow:
History
Introduced in 2010 (8.0) | Updated in 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2017 (11.1) ▪ 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2025 (14.2)
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), ImageKeypoints, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageKeypoints.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "ImageKeypoints." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageKeypoints.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). ImageKeypoints. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageKeypoints.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_imagekeypoints, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ImageKeypoints}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageKeypoints.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_imagekeypoints, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ImageKeypoints}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageKeypoints.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}