URLFetchAsynchronous[url,func]
performs a connection in the background, calling func when an event is raised.




URLFetchAsynchronous
URLFetchAsynchronous[url,func]
performs a connection in the background, calling func when an event is raised.
Details and Options


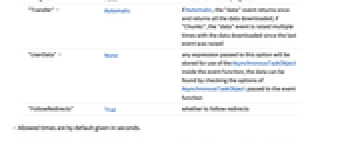
- Types of events that may be raised:
-
"data" returns a list of bytes and indicates that the connection has completed "progress" returns information about the current connection of the form {dlnow,dltotal,ulnow,ultotal} "error" indicates that an error occurred while attempting to connect to a URL "headers" headers received from the web server "cookies" a list of all known cookies "statuscode" the status code returned by the server - The following options can be given:
-
Method "GET" method to use for request "Parameters" {} parameters to be sent for the request "Body" "" contents of message body to be sent "MultipartElements" {} list of multipart data elements to send "Username" "" username to use for the request "Password" "" password to use for the request "Headers" {} headers to be manually sent to the HTTP server "Cookies" Automatic cookies to pass to the server "StoreCookies" True whether to store received cookies "VerifyPeer" True verify authenticity using SSL certificates "UserAgent" Automatic user agent string to send "ReadTimeout" 0 time to allow for uploading or downloading data "ConnectTimeout" 0 time to allow for connecting to the server "Progress" False whether to raise a "progress" event "Transfer" Automatic if Automatic, the "data" event returns once and returns all the data downloaded; if "Chunks", the "data" event is raised multiple times with the data downloaded since the last event was raised "UserData" None any expression passed to this option will be stored for use of the AsynchronousTaskObject inside the event function; the data can be found by checking the options of AsynchronousTaskObject passed to the event function "FollowRedirects" True whether to follow redirects - Allowed times are by default given in seconds.
- Multipart elements must be of the form {"name","mimetype"}->val, where val is a string or a list of bytes.
- When an event is raised, the event function passed to URLFetchAsynchronous will be executed. The event functions will be passed three arguments, the AsynchronousTaskObject, the event name, and the data received from the event. Event functions are the only method for handling data received from URLFetchAsynchronous.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Options (16)
"StoreCookies" (1)
If False, "StoreCookies" will not place any new cookies found while connecting to the site in the global cookie share:
"ReadTimeout" (1)
"ConnectTimeout" (1)
"Progress" (1)
If True, the "progress" event will be raised, returning information downloaded and uploaded about in-progress downloads:
"Transfer" (1)
Properties & Relations (1)
Use URLSaveAsynchronous to store output in a file:
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), URLFetchAsynchronous, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/URLFetchAsynchronous.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "URLFetchAsynchronous." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/URLFetchAsynchronous.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). URLFetchAsynchronous. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/URLFetchAsynchronous.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_urlfetchasynchronous, author="Wolfram Research", title="{URLFetchAsynchronous}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/URLFetchAsynchronous.html}", note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_urlfetchasynchronous, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={URLFetchAsynchronous}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/URLFetchAsynchronous.html}, note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}