WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
AllostericControlExample model showcasing how allosteric control works using the ATCase pathway. |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.ComputationalBiology.AllostericControl"]
Information
Library Dependency
This model requires the BioChem library.
- The free BioChem library is an extendable, general purpose Modelica library for modeling, simulation and visualization of biological and biochemical systems. The library is designed to be used together with Wolfram System Modeler, which enables several extra features such as Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML) import and export. BioChem can, for instance, be used for selecting drug targets with PK/PD modeling or searching for novel drug targets with mechanistic modeling of the reactions in a cell or organism.
Model
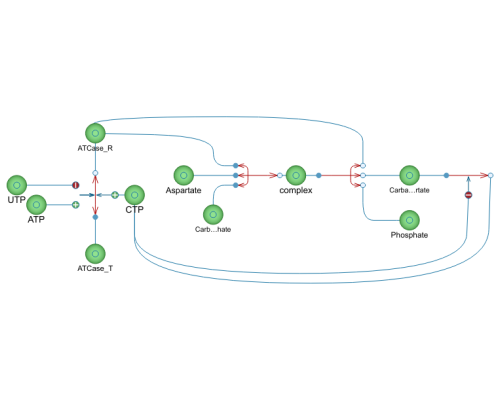
This model illustrates the functions of an allosteric enzyme, aspartate carbamoyltransferase (ATCase), and how its activity is affected both by negative feedback regulation and pure modifiers.
The example model consists of the vital substances in the ATCase reaction. Aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate react in an allosterically catalyzed reaction to become carbamoyl aspartate and phosphate. Carbamoyl aspartate is then further transformed into cytidine triphosphate (CTP), in a reaction that in reality consists of several steps that here have been condensed into one. CTP then, together with uridine triphosphate (UTP), inhibits the reaction and decreases the reaction rate by favoring the tense state of ATCase. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) counters this by instead favoring the relaxed state.
Simulation
Simulating the model allows you to look at how the different substances change over time, and how they are affected by each other. In order to properly analyze this model, it is recommended to use the Wolfram Language notebook that came with this model when it was downloaded. If you prefer to analyze the model in System Modeler, then follow the guide below.
Simulate the model by clicking the Simulate button:
When the simulation is finished and Simulation Center has been opened, you can analyze the result by clicking the various states to the left of the Simulation Center window and selecting the proper value to analyze, for example, Aspartate.c for changes in aspartate concentration over time or ATCase.der for changes in the derivative of ATCase over time.
To analyze the model based on a different initial parameter set than the default, select the state you want to edit in the Model Center and change the desired initial value under Initialization in the General tab. It can also be done directly from Simulation Center, under the Variables tab.
In order to get the full experience of this example, you need a desktop Wolfram Language product. A free trial download is available at www.wolfram.com/mathematica/trial/
For the full example, open the accompanying notebook AllostericControl.nb.
Parameters (4)
| mainCompartment |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: Specifies whether the compartment is a main (top-level) compartment. Used in SBML import/export. |
|---|---|
| kOn |
Value: 10 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Reaction rate for forward enzyme - substrate binding |
| kOff |
Value: 1 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Reaction rate for reverse enzyme - substrate binding |
| kCat |
Value: 1 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Reaction rate for enzyme catalyzed reaction |
Components (14)
| Phosphate |
Type: Substance Description: By-product from the reaction. |
|
|---|---|---|
| Carbamoyl_Aspartate |
Type: Substance Description: Intermediate reactant of the pyrimidine metabolism. |
|
| Carbamoyl_Phosphate |
Type: Substance Description: Reactant that together with asparatate forms carbomyl asparatate. Here the concentration is high enough to not limit the reaction. |
|
| CTP |
Type: Substance Description: Cytidine triphosphate, pushes ATCase towards its tense state. |
|
| finalStep |
Type: Uuifi Description: Final step of the pyrimidine metabolism, forms CTP (cytidine triphosphate). |
|
| Aspartate |
Type: Substance Description: Main reactant, forming carbomyl aspartate when bound to ATCase and carbomyl phosphate. |
|
| ATCase_T |
Type: Substance Description: Tense state of ATCase, almost no affinity for aspartate. |
|
| ATCase_R |
Type: Substance Description: Relaxed state of ATCase, high affinity of aspartate. |
|
| ATP |
Type: Substance Description: Adenosine triphosphate, pushes ATCase towards its relaxed state. |
|
| enzymeSubstrateBidning |
Type: Tur Description: Reversiable reaction that bind the substate together with a free enzyme, forming a complex. |
|
| complex |
Type: Substance Description: ATCase, aspartate and carbomyl phosphat complex. |
|
| enzymeReaction |
Type: Uti Description: Reaction that forms the product and releases the enzyme from the binding. |
|
| UTP |
Type: Substance Description: Uridine triphosphate, pushes ATCase towards its tense state. |
|
| conformationEquilibrium |
Type: Uurfafiba Description: Equlibrium reaction under allosteric control, regulated by UTP, ATP and CTP. |