WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
EnzymeCatalysisModel shows a standard enzyme reaction |
|
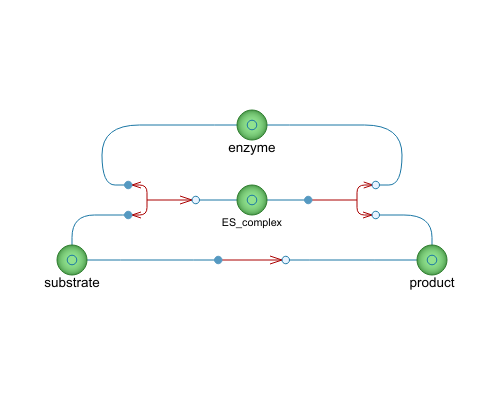
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.ComputationalBiology.EnzymeCatalysis"]
Information
Library Dependency
This model requires the BioChem library.
- The free BioChem library is an extendable, general purpose Modelica library for modeling, simulation and visualization of biological and biochemical systems. The library is designed to be used together with Wolfram System Modeler, which enables several extra features such as Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML) import and export. BioChem can, for instance, be used for selecting drug targets with PK/PD modeling or searching for novel drug targets with mechanistic modeling of the reactions in a cell or organism.
Model
This model illustrates a standard enzyme reaction, together with a non-enzymatic, alternative reaction path. Most enzymes are proteins, and they increase the rate of reactions in organisms by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction. Without enzymes, some processes in the human body would take days, some even decades. Defective enzymes are linked to a number of different diseases and medical conditions such as lactose intolerance.
The example model consists of a two-pathway reaction model, an enzymatic and a non-enzymatic reaction. The enzymatic reaction by default has a rate one million times higher than the non-enzymatic one.
Simulation
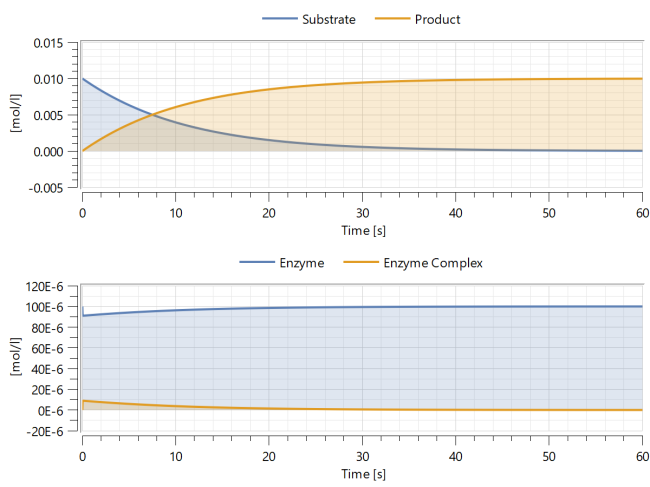
Simulating the model will make it possible to see how the enzyme concentration affects the reaction rate.
Simulate the model by clicking the Simulate button:
If you want to see how a change in enzyme concentration, rate constant or anything else would affect the model, this is possible. To change the initial conditions, you can edit the values of Sc0, Pc0 and Ec0 n the Parameters tab to change the initial substrate, product or enzyme concentration. Modify the corresponding initial concentration or parameter that you would like to change and then click the Simulate button again.
Advanced
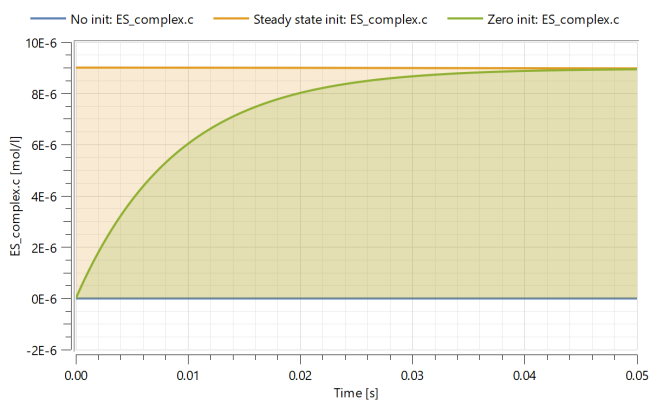
In the model, you can change how the enzyme complex is initialized. The default behavior is to initialize the enzyme complex with zero concentration. This corresponds to a situation were the enzyme and subtrate are quickly mixed together. By changing the enzymeInitialization parameter, you can force the concentrations to instead initialize in steady-state.
In order to get the full experience of this example, you need a desktop Wolfram Language product. A free trial download is available at www.wolfram.com/mathematica/trial/
For the full example, open the accompanying notebook EnzymeCatalysis.nb.
Parameters (8)
| mainCompartment |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: Specifies whether the compartment is a main (top-level) compartment. Used in SBML import/export. |
|---|---|
| kOn |
Value: 1000 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Association coefficient for enzyme-substrate binding reaction (L/(mol·s)) |
| kOff |
Value: 1 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Disassociation coefficient for enzyme-substrate binding reaction (1/s) |
| kCat |
Value: 100 Type: ReactionCoefficient Description: Reaction rate coefficient for enzyme reaction (1/s) |
| Sc0 |
Value: 0.01 Type: Concentration (mol/l) Description: Initial concentration of substrate |
| Pc0 |
Value: 0 Type: Concentration (mol/l) Description: Initial concentration of product |
| Ec0 |
Value: 0.0001 Type: Concentration (mol/l) Description: Initial concentration of enzymes |
| enzymeInitialization |
Value: Init.Zero Type: Init Description: Initialization options for the enzyme reaction, see documentation |
Components (7)
| enzyme |
Type: Substance Description: The enzyme provide a lower energy reaction path for the reaction by stabilizing the transition state, greatly increasing the reaction rate. |
|
|---|---|---|
| substrate |
Type: Substance Description: Defined as a reactant that is consumed in a enzymatic (or catalytic) reaction. |
|
| bur |
Type: Bur Description: The reversible, first reaction in the short reaction chain from substrate to product. |
|
| ES_complex |
Type: Substance Description: The enzyme-substrate complex. The enzyme reversibly binds the substrate, stabilizing its transition state. |
|
| product |
Type: Substance Description: The resulting substance of the reaction. |
|
| ubi |
Type: Ubi Description: The second reaction in the short reaction chain from substrate into product. |
|
| uui |
Type: Uui Description: The non-catalyzed reaction, with a rate several thousand times slower than the enzymatic reaction. |