WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
CamShapesModel exploring three different cam shapes. |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.MechanicalEngineering.CamFollower.CamShapes"]
Information
Dynamics
The follower is modeled as a spring that is attached to a fixed point on one end and that is being pressed against the cam in the other. The cam translates the rotary motion that is being supplied by the rotor to a translational movement that acts on the follower.
Simulation
To simulate the model, click the Simulate button in the top toolbar:
Plot the results
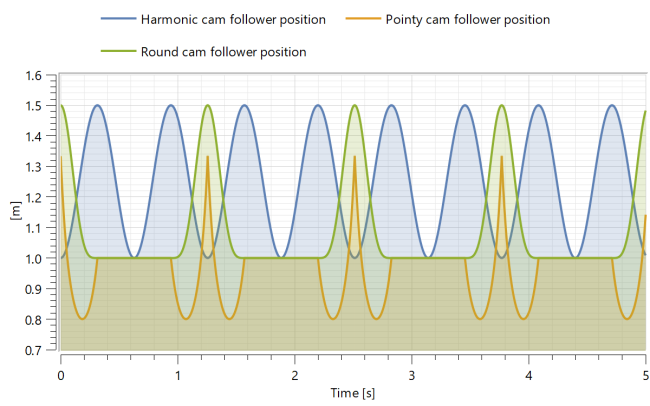
Explore how the follower position changes over time by plotting the variables roundCam.follower.flange_a.s, pointyCam.follower.flange_a.s and harmonicCam.follower.flange_a.s
These variables are shown in the default plot of the model:
Add more plots
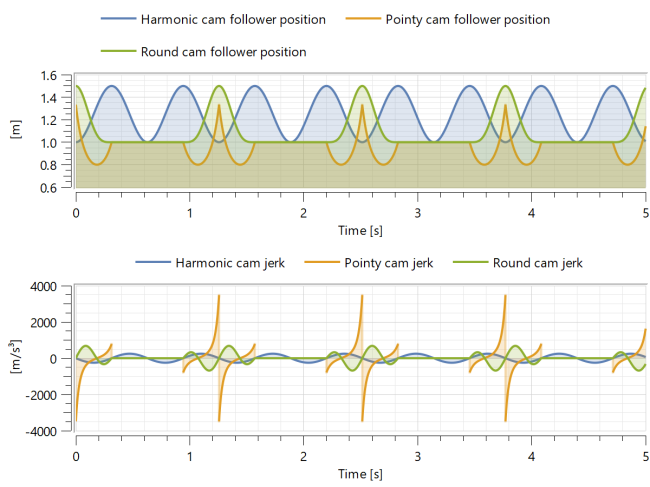
Cam designers wants to minimize the jerk (the derivative of the acceleration), in order to minimize the stress and wear on the cam. Plot the jerking movement and compare it to the follower position. To add a graph of the jerking movement, follow these steps:
Click the New Subplot button in the top toolbar:
From the Model Plots list, drag the plot Cam jerk into the new, empty subplot.
You should see something like the graph below.
In order to get the full experience of this example, you need a desktop Wolfram Language product. A free trial download is available at www.wolfram.com/mathematica/trial/
For the full example, open the accompanying notebook CamFollower.nb.
Components (3)
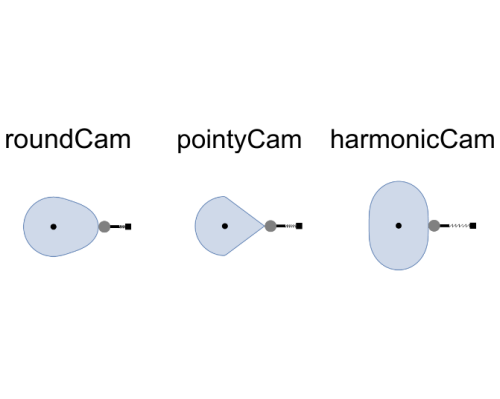
| harmonicCam |
Type: CamHarmonicFollower Description: Harmonic cam shape. Created from the Wolfram Language. |
|
|---|---|---|
| pointyCam |
Type: CamPointyFollower Description: Pointy cam shape. Created from the Wolfram Language. |
|
| roundCam |
Type: CamRoundFollower Description: Round cam shape. Created from the Wolfram Language. |