LaplaceTransform[f[t],t,s]
gives the symbolic Laplace transform of f[t] in the variable t as F[s] in the variable s.
LaplaceTransform[f[t],t,![]() ]
]
gives the numeric Laplace transform at the numerical value ![]() .
.
LaplaceTransform[f[t1,…,tn],{t1,…,tn},{s1,…,sn}]
gives the multidimensional Laplace transform of f[t1,…,tn].




LaplaceTransform
LaplaceTransform[f[t],t,s]
gives the symbolic Laplace transform of f[t] in the variable t as F[s] in the variable s.
LaplaceTransform[f[t],t,![]() ]
]
gives the numeric Laplace transform at the numerical value ![]() .
.
LaplaceTransform[f[t1,…,tn],{t1,…,tn},{s1,…,sn}]
gives the multidimensional Laplace transform of f[t1,…,tn].
Details and Options


- Laplace transforms are typically used to transform differential and partial differential equations to algebraic equations, solve and then inverse transform back to a solution.
- Laplace transforms are also extensively used in control theory and signal processing as a way to represent and manipulate linear systems in the form of transfer functions and transfer matrices. The Laplace transform and its inverse are then a way to transform between the time domain and frequency domain.
- The Laplace transform of a function
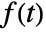 is defined to be
is defined to be 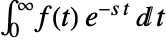 .
. - The multidimensional Laplace transform is given by
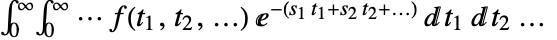 .
. - The integral is computed using numerical methods if the third argument, s, is given a numerical value.
- The asymptotic Laplace transform can be computed using Asymptotic.
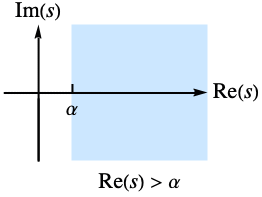
- The Laplace transform of
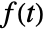 exists only for complex values of s in a half-plane
exists only for complex values of s in a half-plane 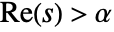 .
. - The lower limit of the integral is effectively taken to be
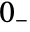 , so that the Laplace transform of the Dirac delta function
, so that the Laplace transform of the Dirac delta function 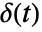 is equal to 1. »
is equal to 1. » - The following options can be given:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic digits of absolute accuracy sought Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate answers that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic method to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to optimize PrecisionGoal Automatic digits of precision sought PrincipalValue False whether to find Cauchy principal value WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations - Use GenerateConditions"ConvergenceRegion" to obtain the region of convergence for the Laplace transform.
- In TraditionalForm, LaplaceTransform is output using
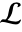 . »
. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (67)
Basic Uses (4)
Laplace transform of a function for a symbolic parameter s:
Laplace transforms of trigonometric functions:
Evaluate the Laplace transform for a numerical value of the parameter s:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Elementary Functions (13)
Laplace transform of a power function:
Laplace transforms of polynomials:
Product of an exponential and a linear function:
Expressions involving trigonometric functions:
Expressions involving hyperbolic functions:
Ratio of an exponential and a linear function:
Ratio of sine and linear functions:
Composition of elementary functions:
Special Functions (10)
Piecewise Functions (9)
Periodic Functions (5)
Laplace transform of SquareWave:
Generalized Functions (5)
Laplace transform of HeavisideTheta:
Derivative of DiracDelta:
Multivariate Functions (9)
Formal Properties (6)
Numerical Evaluation (3)
Calculate the Laplace transform at a single point:
Alternatively, calculate the Laplace transform symbolically:
Then evaluate it for specific value of ![]() :
:
Plot the Laplace transform using numerical values only:
For some functions, the Laplace transform cannot be evaluated symbolically:
Evaluate the Laplace transform numerically and plot it:
Calculate a multivariate Laplace transform at a single point in the plane:
Fractional Calculus (3)
Laplace transform of the MittagLefflerE functions:
ComplexPlot in the ![]() -domain:
-domain:
Inverse Laplace transform to the time domain:
Laplace transform of the MittagLefflerE functions involving parameters:
Inverse Laplace transform to the time domain:
Laplace transform of the CaputoD fractional derivative:
Compare this with the LaplaceTransform of the CaputoD derivative of the sine function:
Options (4)
Assumptions (1)
Specify the range for a parameter using Assumptions:
GenerateConditions (1)
Use GenerateConditions->True to get parameter conditions for when a result is valid:
Principal Value (1)
The Laplace transform of the following function is not defined due to the singularity at ![]() :
:
Use PrincipalValue to obtain the Cauchy principal value for the integral:
Working Precision (1)
Use WorkingPrecision to obtain a result with arbitrary precision:
Applications (12)
Ordinary Differential Equations (5)
Solve a differential equation using Laplace transforms:
Solve for the Laplace transform:
Find the solution directly using DSolve:
Solve the following differential equation:
Solve for the Laplace transform:
Solve an RL circuit to find the current ![]() :
:
Verify with DSolveValue:
Green's function for an RL circuit:
Fractional Differential Equations (3)
Solve a fractional-order differential equation using Laplace transforms:
Solve for the Laplace transform:
Find the solution directly using DSolve:
Solve the following fractional integro-differential equation:
Solve for the Laplace transform:
Find the solution directly using DSolve:
The following equation describes a fractional harmonic oscillator of order 1.9:
Solve for the Laplace transform:
Find the solution directly using DSolve:
Evaluation of Integrals (2)
Calculate the following integral:
Compute the Laplace transform and interchange the order of Laplace transform and integration:
Perform the integration over ![]() :
:
Use InverseLaplaceTransform to obtain the original integral:
Integral involving the Bessel function:
Perform a change of variables ![]() and introduce an auxiliary variable
and introduce an auxiliary variable ![]() :
:
Apply the Laplace transform and interchange the order of Laplace transform and integration:
Perform the integration over ![]() :
:
Use InverseLaplaceTransform to obtain ![]() :
:
Other Applications (2)
Compute a Laplace transform using a series expansion:
The transformed series can be summed using Regularization:
Verify the result directly using LaplaceTransform:
Laplace transform of Sinc using series expansions:
Properties & Relations (3)
Use Asymptotic to compute an asymptotic approximation:
LaplaceTransform and InverseLaplaceTransform are mutual inverses:
Use NIntegrate for numerical approximation:
NIntegrate computes the transform for numeric values of the Laplace parameter s:
Neat Examples (2)
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1999 (4.0) | Updated in 2020 (12.2) ▪ 2023 (13.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (1999), LaplaceTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LaplaceTransform.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1999. "LaplaceTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LaplaceTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1999). LaplaceTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LaplaceTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_laplacetransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{LaplaceTransform}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LaplaceTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-December-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_laplacetransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={LaplaceTransform}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LaplaceTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-December-2025]}