MathieuC[a,q,z]
gives the even Mathieu function with characteristic value a and parameter q.


MathieuC
MathieuC[a,q,z]
gives the even Mathieu function with characteristic value a and parameter q.
Details
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- The Mathieu functions satisfy the equation
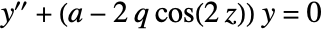 .
. - For certain special arguments, MathieuC automatically evaluates to exact values.
- MathieuC can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- MathieuC automatically threads over lists.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (21)
Numerical Evaluation (5)
Evaluate numerically to high precision:
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate for complex arguments and parameters:
Evaluate MathieuC efficiently at high precision:
MathieuC threads elementwise over lists:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix MathieuC function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (4)
Simple exact values are generated automatically:
Find a local maximum as the root of ![]() in the maximum's neighborhood:
in the maximum's neighborhood:
MathieuC is an even function:
Visualization (3)
Function Properties (4)
Differentiation (3)
Applications (3)
This differential equation is solved in terms of MathieuC and MathieuS functions:
Solve the Schrödinger equation with periodic potential:
By the Bloch theorem, solutions are bounded provided ![]() is within an energy band. The energy gap corresponds to a range of
is within an energy band. The energy gap corresponds to a range of ![]() where MathieuCharacteristicExponent has a non-vanishing imaginary part:
where MathieuCharacteristicExponent has a non-vanishing imaginary part:
Solve the Laplace equation in an ellipse using separation of variables:
This plots an eigenfunction. It vanishes at the ellipse boundary:
See Also
MathieuS MathieuCPrime MathieuCharacteristicA HeunC LameC
Function Repository: MathieuEllipticCos
Tech Notes
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1996 (3.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1996), MathieuC, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MathieuC.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1996. "MathieuC." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MathieuC.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1996). MathieuC. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MathieuC.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_mathieuc, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MathieuC}", year="1996", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MathieuC.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-January-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_mathieuc, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MathieuC}, year={1996}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MathieuC.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-January-2026]}