PoolingLayer[sz]
represents a pooling net layer using kernels of size sz.
PoolingLayer[{w}]
represents a layer performing one-dimensional pooling with kernels of size w.
PoolingLayer[{h,w}]
represents a layer performing two-dimensional pooling with kernels of size h×w.
PoolingLayer[{h,w,d}]
represents a layer performing three-dimensional pooling with kernels of size h×w×d.
PoolingLayer[kernel,stride]
represents a layer that uses stride as the step size between kernel applications.
PoolingLayer[kernel,opts]
includes options for other pooling methods, padding and other parameters.


PoolingLayer
PoolingLayer[sz]
represents a pooling net layer using kernels of size sz.
PoolingLayer[{w}]
represents a layer performing one-dimensional pooling with kernels of size w.
PoolingLayer[{h,w}]
represents a layer performing two-dimensional pooling with kernels of size h×w.
PoolingLayer[{h,w,d}]
represents a layer performing three-dimensional pooling with kernels of size h×w×d.
PoolingLayer[kernel,stride]
represents a layer that uses stride as the step size between kernel applications.
PoolingLayer[kernel,opts]
includes options for other pooling methods, padding and other parameters.
Details and Options




- PoolingLayer[n,…] represents a layer that, applied to an input array with c input channels and one or more spatial dimensions, performs c distinct pooling operations across the spatial dimensions to produce an output array with c channels.
- PoolingLayer[n] is equivalent to PoolingLayer[n,1].
- The following optional parameters can be included:
-
"Dimensionality" Automatic number of spatial dimensions of the pooling "Function" Max aggregation function to use Interleaving False the position of the channel dimension PaddingSize 0 amount of zero padding to apply to the input - With the setting InterleavingFalse, the channel dimension is taken to be the first dimension of the input and output arrays.
- With the setting InterleavingTrue, the channel dimension is taken to be the last dimension of the input and output arrays.
- The settings for kernel and stride can be of the following forms:
-
n use the value n for all dimensions {…,ni,…} use the value ni for the i 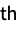 dimension
dimension - The setting for PaddingSize can be of the following forms:
-
n pad every dimension with n zeros on the beginning and end {n1,n2,…} pad the i 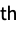 dimension with n zeros on the beginning and end
dimension with n zeros on the beginning and end{{n1,m1},{n2,m2},…} pad the i 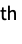 dimension with ni zeros at the beginning and mi zeros at the end
dimension with ni zeros at the beginning and mi zeros at the end"Same" - pad every dimension so that the output size is equal to the input size divided by the stride (rounded up)
- PoolingLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer.
- PoolingLayer[…][{input1,input2,…}] explicitly computes outputs for each of the inputi.
- When given a NumericArray as input, the output will be a NumericArray.
- PoolingLayer is typically used inside NetChain, NetGraph, etc.
- NetExtract can be used to extract parameter values from a PoolingLayer object.
- PoolingLayer exposes the following ports for use in NetGraph etc.:
-
"Input" an array of rank 2, 3 or 4 "Output" an array of rank 2, 3 or 4 - PoolingLayer can operate on arrays that contain "Varying" dimensions.
- Possible explicit settings for the "Function" option include:
-
Max the maximum is used Mean the mean value is used Total the sum of all values is used - When it cannot be inferred from other layers in a larger net, the option "Input"->{d1,…,dn} can be used to fix the input dimensions of PoolingLayer.
- Given an input array of dimensions d1×…×di×…, the output array will be of dimensions
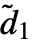 ×…×
×…×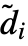 ×…, where the channel dimension remains unchanged (i.e. d1=
×…, where the channel dimension remains unchanged (i.e. d1=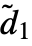 ) and the sizes of spatial dimensions are transformed according to
) and the sizes of spatial dimensions are transformed according to 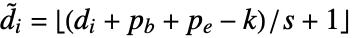 , where
, where 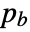 /
/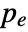 are the padding sizes at the beginning/end of the axis,
are the padding sizes at the beginning/end of the axis, 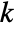 is the kernel size, and
is the kernel size, and 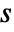 is the stride size for each dimension.
is the stride size for each dimension. - Options[PoolingLayer] gives the list of default options to construct the layer. Options[PoolingLayer[…]] gives the list of default options to evaluate the layer on some data.
- Information[PoolingLayer[…]] gives a report about the layer.
- Information[PoolingLayer[…],prop] gives the value of the property prop of PoolingLayer[…]. Possible properties are the same as for NetGraph.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a PoolingLayer with a kernel size of 5×5:
Create a one-dimensional PoolingLayer:
Scope (4)
Create a one-dimensional PoolingLayer with a stride of 4 and apply it to an input:
Create an initialized three-dimensional PoolingLayer with kernel size 2:
Apply the layer to an input array:
Create a two-dimensional PoolingLayer with a non-symmetric stride and apply it to an input:
Create a two-dimensional PoolingLayer that takes an image and returns an image:
Options (6)
"Function" (2)
Interleaving (1)
Create a PoolingLayer with InterleavingFalse and one input channel:
Create a PoolingLayer with InterleavingTrue and one input channel:
PaddingSize (3)
Create a two-dimensional PoolingLayer that pads the first dimension with 10 zeros on each side and the second dimension with 12 zeros on each side:
Create a two-dimensional PoolingLayer that pads the first dimension with 10 zeros at the beginning and 14 zeros at the end:
Use padding to make the output dimensions equivalent to the input dimensions:
Properties & Relations (2)
The following function computes the size of the non-channel dimensions, given the input size and parameters:
The output size of an input of size {256,252}, a kernel size of 3, a stride of 2, and padding size of 2:
This agrees with defining a PoolingLayer with the same parameters:
Increasing the stride can decrease the evaluation time of PoolingLayer:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2016 (11.0) | Updated in 2017 (11.1) ▪ 2018 (11.3) ▪ 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), PoolingLayer, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoolingLayer.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "PoolingLayer." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoolingLayer.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). PoolingLayer. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoolingLayer.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_poolinglayer, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PoolingLayer}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoolingLayer.html}", note=[Accessed: 03-November-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_poolinglayer, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PoolingLayer}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoolingLayer.html}, note=[Accessed: 03-November-2025]}