EulerPhi[n]
gives the Euler totient function ![]() .
.


EulerPhi
EulerPhi[n]
gives the Euler totient function ![]() .
.
Details
- EulerPhi is also known as the Euler totient function or phi function.
- Integer mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- Typically used in cryptography and in many applications in elementary number theory.
- EulerPhi[n] counts positive integers up to n that are relatively prime to n.
- For a number
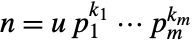 with
with 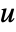 a unit and
a unit and 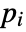 primes, EulerPhi[n] gives
primes, EulerPhi[n] gives 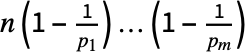 .
.
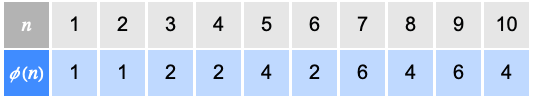
Examples
open all close allScope (9)
Numerical Evaluation (4)
EulerPhi threads over lists:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Symbolic Manipulation: (5)
Solve equations involving EulerPhi:
Use FullSimplify with EulerPhi:
Use FunctionExpand with EulerPhi:
FindSequenceFunction can recognize the EulerPhi sequence:
Applications (9)
Basic Applications (4)
Length of the nth-order FareySequence can be expressed in terms of EulerPhi:
Power series of the generating function for GCD:
Count the number of primes using EulerPhi:
Number Theory (5)
Model Fleck's totient function:
![]() reproduces the Euler totient function:
reproduces the Euler totient function:
Generalizations and closed forms:
Plot the cumulative sum of EulerPhi:
Compare with an asymptotic approximation:
First several ![]() -s where the difference
-s where the difference ![]() is negative:
is negative:
The probability that two randomly chosen positive integers less than x are relatively prime:
Compare with the asymptotic limit:
Build RSA-like encryption scheme. Start with the modulus:
Find the universal exponent of the multiplication group modulo n:
Number of cyclic necklaces of length n that can be formed with b types of beads:
Properties & Relations (11)
EulerPhi is non-negative:
EulerPhi is a multiplicative function:
For any prime number p and natural number r, ϕ(pr)=pr-pr-1:
Similarly, EulerPhi[n]==n∏p|n(1-1/p) where p is prime:
Alternatively, EulerPhi[n]==n∑k|nMoebiusMu[k]/k:
CarmichaelLambda divides EulerPhi:
When n is a prime power, they are equal:
For a Cyclotomic field, the NumberFieldDiscriminant can be found using EulerPhi:
If ![]() has a primitive root, then CarmichaelLambda and EulerPhi are the same:
has a primitive root, then CarmichaelLambda and EulerPhi are the same:
Determine EulerPhi through prime factorization:
For any square-free number n, the totient of n is equal to the product of the totients of each factor of n :
Neat Examples (4)
Form an absolutely abnormal number as the limit of the following sequence:
Digits of the sixth approximation in various bases:
Iterate the map ![]() and display result modulo
and display result modulo ![]() :
:
Plot of Ulam spiral where numbers are colored based on the values of EulerPhi:
See Also
MultiplicativeOrder CarmichaelLambda PowerMod CoprimeQ FactorInteger GCD LCM Divisors PrimeQ SquareFreeQ PrimePowerQ MoebiusMu
Function Repository: JordanTotient RamanujanC Totatives
Tech Notes
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), EulerPhi, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/EulerPhi.html (updated 2007).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "EulerPhi." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2007. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/EulerPhi.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). EulerPhi. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/EulerPhi.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_eulerphi, author="Wolfram Research", title="{EulerPhi}", year="2007", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/EulerPhi.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_eulerphi, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={EulerPhi}, year={2007}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/EulerPhi.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}