

Map 
Details and Options
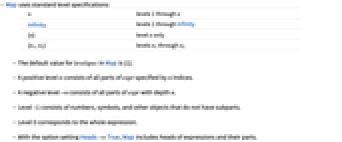
- Map uses standard level specifications:
-
n levels 1 through n Infinity levels 1 through Infinity {n} level n only {n1,n2} levels n1 through n2 - The default value for levelspec in Map is {1}.
- A positive level n consists of all parts of expr specified by n indices.
- A negative level -n consists of all parts of expr with depth n.
- Level –1 consists of numbers, symbols, and other objects that do not have subparts.
- Level 0 corresponds to the whole expression.
- With the option setting Heads->True, Map includes heads of expressions and their parts.
- Map always effectively constructs a complete new expression and then evaluates it.
- If expr is an Association object, Map[f,expr] applies f to the values in the association. »
- If expr is a SparseArray object or structured array, Map[f,expr] applies f to the values or subarrays that appear in expr. »
- Map[f][expr] is equivalent to Map[f,expr].
- Parallelize[Map[f,expr]] or ParallelMap[f,expr] computes Map[f,expr] in parallel on all subkernels. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Evaluate f on each element of a list:
Map a function over values in Association:
Scope (11)
Level Specifications (6)
Types of Expressions (5)
Map can be used on expressions with any head:
Map can be used on sparse arrays:
Use Map with structured arrays, such as SymmetrizedArray:
Use Map to apply a function to the elements of a structured array of type QuantityArray:
Map at the second level of a nested Association:
Map at several levels in an Association:
Applications (4)
Properties & Relations (9)
A function of several arguments can be mapped with MapThread:
MapIndexed passes the index of an element to the mapped function:
MapAll is equivalent to a specific level specification in Map:
Scan does the same as Map, but without returning a result:
Functions with attribute Listable are mapped automatically:
ParallelMap computes Map in parallel:
Map can be parallelized automatically, effectively using ParallelMap:
Map wraps an expression around parts of another expression:
Comap wraps parts of an expression around another expression:
Map maps a function over the values in an association:
KeyMap maps a function over the keys in an association:
KeyValueMap maps a function over the keys and values in an association (and returns a list):
AssociationMap maps a function over the rules in an association:
Map[f,assoc] is equivalent to AssociationThread[Keys[assoc]Map[f,Values[assoc]]]:
Possible Issues (1)
Map by default starts at level 1, so does not apply the function to the whole expression:
See Also
Apply Scan MapAll MapAt MapIndexed MapApply MapThread SubsetMap AssociationMap KeyMap KeyValueMap ParallelMap Level Operate Comap Through Thread ImageApply
Function Repository: MapCases MapBatched JoinMap
Tech Notes
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2003 (5.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Map, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Map.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Map." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Map.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Map. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Map.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_map, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Map}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Map.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_map, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Map}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Map.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}