Reaction
2D/3D• Reaction[cnum, bnum, point] returns the reaction loads applied by constraint cnum to body bnum, calculated about the specified point. Loads are returned in the format: {force, moment}.
• Reaction[cnum, bnum] returns the reaction loads calculated about the local origin of body bnum.
• Reaction accepts the Coordinates option specify whether the resulting load vectors are in Global or body Local coordinates.
• Reaction is also a setting for the Type option for Loads.
• Type->Reaction causes Loads to return the total kinematic reaction forces applied to a body. • Reaction[cnum, Point[bnum, lpnt]] returns the reaction force applied by constraint cnum to body bnum, calculated about local point lpnt on body bnum.
• The constraint number specification, cnum, can be replaced with any of the specific constraint equation specifications accepted by Constraints.
• Note that only the reaction moment is a function of the location of point. Reaction forces are not dependent on the point about which they are calculated.
• The default option setting is Coordinates->Global.
• Reaction[cnum, symbol] returns the reaction applied by constraint cnum to a particular symbol, in consistent force or moment units. The symbol must be a coordinate or parameter that occurs in the current model's constraint equations.
• The meaning of the quantity returned by Reaction[cnum, symbol] depends on the nature of the occurrence of symbol in the model. For example, if a parameter named len specifies the length of a simple connecting link in the mechanism, the value of Reaction[All, len] corresponds to the tension in the connecting link.
• If symbol occurs in the model in a very complicated and interlinked manner the value returned by Reaction has little physical meaning.
• The alternatives to the Reaction setting for the Type option are Applied and Dynamic, which cause Loads to return external loads or inertial loads, respectively.
• See also: SetLoads. Further Examples Load the Modeler2D package and define a simple model. Here is the total reaction force applied to the link body by all constraints. Note that the numerical value differs if we generate a solution with or without the dynamic loading because the dynamic loading is balanced by the reaction forces.
Out[2]= | 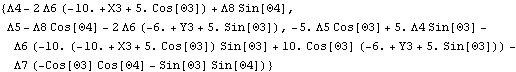 |
Out[3]= | 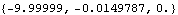 |
Out[4]= | 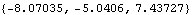 |
The total reaction force given by Loads is identical to summing all the independent reaction forces applied by each constraint associated with the link body.
Out[5]= | 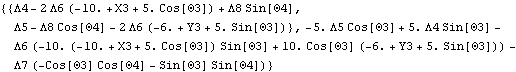 |
See HelpModel2D.
|