NInverseFourierCoefficient[expr,n,t]
gives a numerical approximation to the function, evaluated at t, whose Fourier exponential series representation has coefficients given by expr, where expr is a function of n.
Details and Options


Examples
Basic Examples
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
FourierSeries`
FourierSeries`
NInverseFourierCoefficient
NInverseFourierCoefficient[expr,n,t]
gives a numerical approximation to the function, evaluated at t, whose Fourier exponential series representation has coefficients given by expr, where expr is a function of n.
Details and Options
- To use NInverseFourierCoefficient, you first need to load the Fourier Series Package using Needs["FourierSeries`"].
- The numerical approximation to the Fourier exponential series representation used by NInverseFourierCoefficient is by default defined to be NSum[expr -2πnt,{n,-∞,∞}].
- Different choices for the definition of the Fourier exponential series representation can be specified using the option FourierParameters.
- With the setting FourierParameters->{a,b}, the Fourier exponential series representation used by NInverseFourierCoefficient is
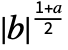 NSum[expr -2 πbnt,{n,-∞,∞}].
NSum[expr -2 πbnt,{n,-∞,∞}]. - The parameter b in the setting FourierParameters->{a,b} must be numeric.
- In addition to the option FourierParameters, NInverseFourierCoefficient can also accept the options available to NSum. These options are passed directly to NSum.