NLimit[expr,z->z0]
numerically finds the limiting value of expr as z approaches z0.
Details and Options


Examples
Basic Examples
Scope
Options
Terms
Scale
Direction
Method
WynnDegree
WorkingPrecision
Applications
Properties & Relations
Possible Issues
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
NumericalCalculus`
NumericalCalculus`
NLimit
NLimit[expr,z->z0]
numerically finds the limiting value of expr as z approaches z0.
Details and Options
- To use NLimit, you first need to load the Numerical Calculus Package using Needs["NumericalCalculus`"].
- The expression expr must be numeric when its argument z is numeric.
- NLimit constructs a sequence of values that approach the point z0 and uses extrapolation to find the limit.
- NLimit is unable to recognize small numbers that should in fact be zero. Chop may be needed to eliminate these spurious residuals.
- NLimit often fails when the limit has a power law approach to infinity.
- The following options can be given:
-
WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision precision to use in internal computations Direction Automatic vector giving the direction of approach Scale 1 initial step size in the sequence of steps Terms 7 number of terms used to evaluate the limit Method EulerSum the method used to evaluate the result WynnDegree 1 degree used in Wynn's epsilon algorithm - The option Direction->d specifies that the approach vector to a finite limit point z0 is given by the complex number d. The default setting Direction->Automatic is equivalent to Direction->-1, and computes the limit as z approaches z0 from larger values.
- NLimit approaches infinite limit points on a ray from the origin.
- The option Scale specifies the initial step in the constructed sequence.
- For finite limit points x0, the initial step is a distance Scale away from x0. For infinite limit points, the initial step is a distance Scale away from the origin.
- The accuracy of the result is generally improved by increasing the number of terms, although increased WorkingPrecision will also usually be necessary.
- Possible settings for Method include:
-
EulerSum converts sequence to a sum and uses EulerSum SequenceLimit uses SequenceLimit on constructed sequence - The option WynnDegree specifies the number of iterations of Wynn's epsilon algorithm to be used by SequenceLimit. In general, there must be at least
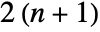 terms for
terms for 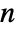 iterations.
iterations.
Examples
open all close allOptions (8)
Terms (2)
Scale (1)
Use Scale to avoid regions where the expression is undefined:
The function ![]() diverges for
diverges for ![]() , so choose the initial step to avoid this divergence:
, so choose the initial step to avoid this divergence:
Direction (1)
Method (2)
WynnDegree (1)
When using Method->SequenceLimit, increasing WynnDegree may improve the accuracy of the limit:
WorkingPrecision (1)
Increasing WorkingPrecision alone does not produce a more accurate result:
Error with WorkingPrecision->20:
Error with WorkingPrecision->30:
To improve accuracy, the number of terms needs to be increased: