DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[ssm,{w,v},τ]
gives the optimal discrete-time estimator gain matrix with sampling period τ for the continuous-time StateSpaceModel ssm, with process and measurement noise covariance matrices w and v.
DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[{ssm,sensors},{w,v},τ]
specifies sensors as the noisy measurements of ssm.
DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[{ssm,sensors,dinputs},{w,v},τ]
specifies dinputs as the deterministic inputs of ssm.


DiscreteLQEstimatorGains
DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[ssm,{w,v},τ]
gives the optimal discrete-time estimator gain matrix with sampling period τ for the continuous-time StateSpaceModel ssm, with process and measurement noise covariance matrices w and v.
DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[{ssm,sensors},{w,v},τ]
specifies sensors as the noisy measurements of ssm.
DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[{ssm,sensors,dinputs},{w,v},τ]
specifies dinputs as the deterministic inputs of ssm.
Details and Options

- The standard state-space model ssm can be given as StateSpaceModel[{a,b,c,d}], where a, b, c, and d represent the state, input, output, and transmission matrices of the continuous-time system
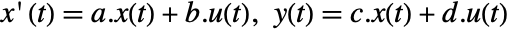 .
. - The descriptor continuous-time state-space model ssm defined by
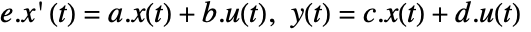 can be given as StateSpaceModel[{a,b,c,d,e}].
can be given as StateSpaceModel[{a,b,c,d,e}]. - The input
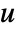 can include the process noise
can include the process noise 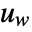 , as well as deterministic inputs
, as well as deterministic inputs  .
. - The argument dinputs is a list of integers specifying the positions of
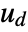 in
in 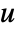 .
. - The output
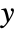 consists of the noisy measurements
consists of the noisy measurements 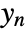 , as well as other outputs.
, as well as other outputs. - The argument sensors is a list of integers specifying the positions of
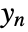 in
in 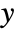 .
. - DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[ssm,{…},τ] is equivalent to DiscreteLQEstimatorGains[{ssm, All,None},{…},τ].
- The noisy measurements are modeled as
 , where
, where 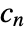 and
and 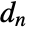 are the submatrices of
are the submatrices of 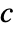 and
and 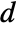 associated with
associated with 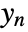 , and
, and 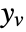 is the noise.
is the noise. - The process and measurement noises are assumed to be white and Gaussian:
-
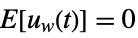 ,
, 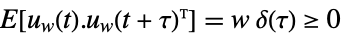
process noise 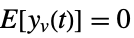 ,
, 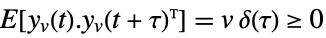
measurement noise - The estimator with the optimal gain minimizes
 , where
, where 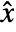 is the estimated state vector.
is the estimated state vector. - DiscreteLQEstimatorGains computes the estimator gains based on the discrete equivalent of the noise matrices.
- The state-space model ssm is discretized using the zero-order hold method.
Examples
open all close allScope (3)
Properties & Relations (1)
Find estimator gains using DiscreteLQEstimatorGains:
Create a discrete-time Kalman estimator with the gains and a discretized model:
This is different from that obtained by discretizing a continuous-time estimator:
Response of the first estimator in the presence of process and measurement noises:
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), DiscreteLQEstimatorGains, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.html (updated 2012).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "DiscreteLQEstimatorGains." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2012. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). DiscreteLQEstimatorGains. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_discretelqestimatorgains, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DiscreteLQEstimatorGains}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_discretelqestimatorgains, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DiscreteLQEstimatorGains}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}