FlatShading
is a three-dimensional graphics directive that specifies that faces of polygons and other filled graphics objects are to be drawn to reflect as a flat surface.
FlatShading[d]
uses the attenuation factor d for the diffuse light.
FlatShading[d,a]
uses the attenuation factor a for the ambient light.
Details

- FlatShading is also known per‐face shading.
- FlatShading is typically used to make individual faces and edges of polygons easily visible.
- The final color of a face of a polygon is computed from the polygon surface normal and the luminosity of the color resulting from standard shading.
- FlatShading[d,a] specifies that the diffuse light on a 3D surface should be attenuated by a factor d and the ambient light by a.
- FlatShading[] is effectively equivalent to FlatShading[1,1].
- The setting Lighting"Accent" uses a directional light and faithfully reproduces colors on the surface.
- The basic shading models FlatShading, GouraudShading and PhongShading compared:

Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (12)
Basic Uses (5)
Specification (4)
FlatShading with no arguments uses similar calculations for diffuse and ambient light as the default system shader:
Attenuate all light from the surface by a scaler value:
This is equivalent to specifying each attenuation factor explicitly:
Attenuate the diffuse light, setting the other attenuation factor to zero:
Attenuate the ambient light, setting the other attenuation factor to zero:
Lighting (3)
FlatShading works with all types of lights:
The ambient percentage only applies if an AmbientLight is has been specified:
Applications (4)
Basic Applications (2)
The face colors are constant across the face of a polygon and based on the face normal:
Apply FlatShading on the Icosahedron:
The face color is based on the angle between the face normal and light vector:
The face is brightest when pointed toward the light:
The face is darkest when the face normal and light vector are orthogonal:
Properties & Relations (3)
FlatShading ignores VertexNormals:
Specify FaceForm with FlatShading:
FlatShading is similar to PhongShading when no VertexNormals are available:
FlatShading does not include specular reflection:
Possible Issues (2)
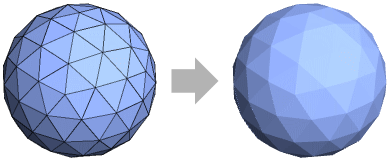
FlatShading works for graphics objects made of flat polygonal faces:
A discretization of the sphere:
Specular reflection does not affect FlatShading:
Use the default system shader with no VertexNormals specified to include specular lighting:
Text
Wolfram Research (2022), FlatShading, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FlatShading.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2022. "FlatShading." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FlatShading.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2022). FlatShading. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FlatShading.html