FullInformationOutputRegulator[sys,rspec]
gives the full state information output regulator for sys using specification rspec.
FullInformationOutputRegulator[{sys,{out1,…},{in1,…}},…]
specifies the regulated outputs outi and the controlled inputs inj.


FullInformationOutputRegulator
FullInformationOutputRegulator[sys,rspec]
gives the full state information output regulator for sys using specification rspec.
FullInformationOutputRegulator[{sys,{out1,…},{in1,…}},…]
specifies the regulated outputs outi and the controlled inputs inj.
Details and Options

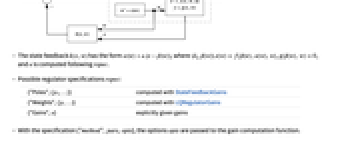
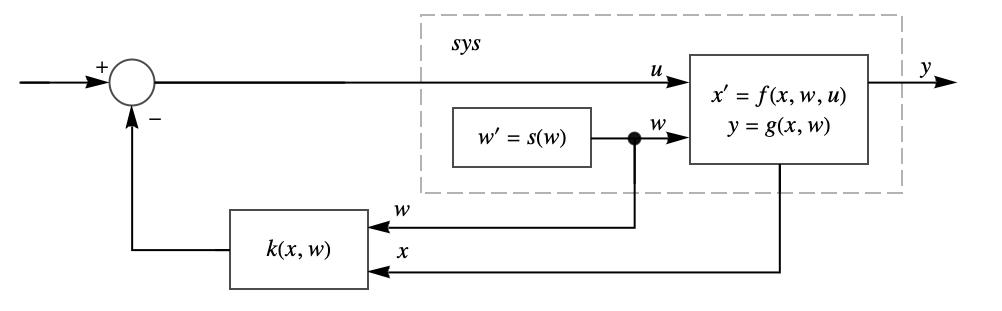
- FullInformationOutputRegulator returns a regulator that drives the sys outputs to zero and is typically used to suppress or track known inputs to the system.
- The system sys is taken to have state equations
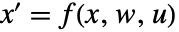 and
and 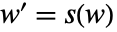 and outputs
and outputs 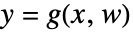 , with
, with 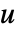 being the controllable input. The state
being the controllable input. The state 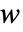 is not affected by the input
is not affected by the input 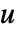 and is used to model signals to suppress or track, as indicated by the output function
and is used to model signals to suppress or track, as indicated by the output function 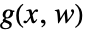 .
. - Typical output functions
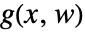 , which the regulator will drive to zero:
, which the regulator will drive to zero: -
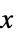
suppress the effects of 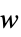 on the states
on the states 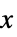
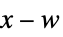
cause 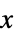 to track
to track 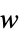
- The system sys can be StateSpaceModel, AffineStateSpaceModel, or NonlinearStateSpaceModel.
- The computed state feedback
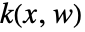 regulates sys about an operating point using
regulates sys about an operating point using 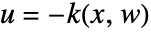 .
. - The state feedback
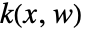 has the form
has the form 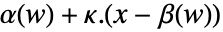 , where
, where 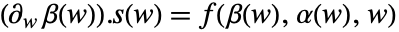 ,
, 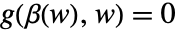 , and
, and 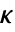 is computed following rspec.
is computed following rspec. - Possible regulator specifications rspec:
-
{"Poles",{p1,…}} computed with StateFeedbackGains {"Weights",{p,…}} computed with LQRegulatorGains {"Gains",κ} explicitly given gains - With the specification {"method",pars,opts}, the options opts are passed to the gain computation function.
- The outputs {out1,…} and inputs {in1,…} are part specifications and by default are taken to be All.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (8)
The regulator for a linear system with the exosystem pole at the origin:
The exosystem has a pair of complex poles:
The exosystem's states are part of the regulator:
The system is regulated if pf is negative:
Regulate an AffineStateSpaceModel:
Regulate a NonlinearStateSpaceModel:
Specify the regulated outputs and feedback inputs:
Use LQRegulatorGains to compute the stabilizing gains by specifying the weights:
Applications (6)
Reject a disturbance modeled as ![]() :
:
The full model of the system with disturbance:
The output is regulated in the presence of the disturbance:
The full model of the system and input model:
Simultaneously track a step input and reject a sinusoidal disturbance:
The simulation shows the output tracking a step signal:
Regulate an aircraft's longitudinal dynamics in the presence of disturbances:»
The disturbances consist of two frequency components:
A control law that regulates the output (speed) in the presence of the disturbances:
Simulation showing regulation being achieved:
Regulate a Rössler prototype-4 system:»
The complete model such that the state ![]() is regulated and kept constant:
is regulated and kept constant:
Simulations show that ![]() is regulated and the system has no chaotic behavior with feedback:
is regulated and the system has no chaotic behavior with feedback:
Regulate the voltage ![]() in a Chua circuit to follow a sinusoid while rejecting a disturbance
in a Chua circuit to follow a sinusoid while rejecting a disturbance ![]() that is the output of another Chua circuit:»
that is the output of another Chua circuit:»
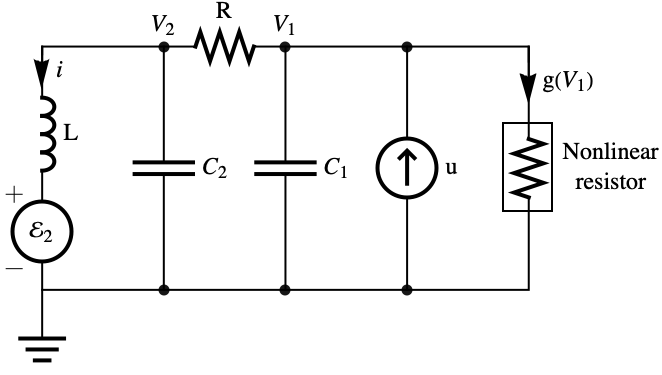
The affine model of the Chua circuit where the nonlinearity is a cubic polynomial:
The exosystem, where ω is the frequency of the sinusoid to be tracked:
The poles of the disturbance model:
The system poles consist of the three new poles and the stabilizable poles:
Properties & Relations (4)
StateFeedbackGains is a special case:
LQRegulatorGains is a special case:
Obtain the closed-loop system using SystemsModelStateFeedbackConnect:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), FullInformationOutputRegulator, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FullInformationOutputRegulator.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "FullInformationOutputRegulator." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FullInformationOutputRegulator.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). FullInformationOutputRegulator. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FullInformationOutputRegulator.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_fullinformationoutputregulator, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FullInformationOutputRegulator}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FullInformationOutputRegulator.html}", note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_fullinformationoutputregulator, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FullInformationOutputRegulator}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FullInformationOutputRegulator.html}, note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}