gives the assortativity coefficient of a graph g using vertex degrees.
GraphAssortativity[g,"prop"]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g using vertex property "prop".
GraphAssortativity[g,{{vi 1,vi 2,…},…}]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g with respect to the vertex partition {{vi 1,vi 2,…},…}.
GraphAssortativity[g,{v1,v2,…}{x1,x2,…}]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g using data {x1,x2,…} for vertices {v1,v2,…}.
GraphAssortativity[{vw,…},…]
uses rules vw to specify the graph g.


GraphAssortativity
gives the assortativity coefficient of a graph g using vertex degrees.
GraphAssortativity[g,"prop"]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g using vertex property "prop".
GraphAssortativity[g,{{vi 1,vi 2,…},…}]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g with respect to the vertex partition {{vi 1,vi 2,…},…}.
GraphAssortativity[g,{v1,v2,…}{x1,x2,…}]
gives the assortativity coefficient of the graph g using data {x1,x2,…} for vertices {v1,v2,…}.
GraphAssortativity[{vw,…},…]
uses rules vw to specify the graph g.
Details and Options

- For a graph with
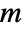 edges and adjacency matrix entries
edges and adjacency matrix entries 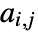 , the assortativity coefficient is given by
, the assortativity coefficient is given by 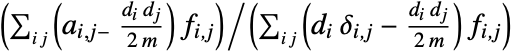 , where
, where 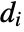 is the out-degree for the vertex vi and
is the out-degree for the vertex vi and 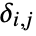 is 1 if there is an edge from vi to vj and 0 otherwise.
is 1 if there is an edge from vi to vj and 0 otherwise. - For quantitative data where x1,x2,… are used,
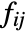 is taken to be xixj.
is taken to be xixj. - For categorical data where x1,x2,… are used,
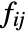 is taken to be 1 if xi and xj are equal and 0 otherwise.
is taken to be 1 if xi and xj are equal and 0 otherwise. - In GraphAssortativity[g], xi is taken to be the vertex out-degree for the vertex vi.
- In GraphAssortativity[g,"prop"], xi is taken to be AnnotationValue[{g,vi},"prop"] for the vertex vi.
- In GraphAssortativity[g,{{vi 1,vi 2,…},…}], vertices in a subset {vi 1,vi 2,…} have the same categorical data xi 1=xi 2=….
- GraphAssortativity[g,Automatic->{x1,x2,…}] takes the vertex list to be VertexList[g].
- The option "DataType"->type can be used to specify the type for the data x1,x2,…. Possible settings are "Quantitative" and "Categorical".
- The option "Normalized"->False can be used to compute the assortativity modularity.
- For a graph with
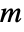 edges and adjacency matrix entries
edges and adjacency matrix entries 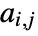 , the assortativity modularity is given by
, the assortativity modularity is given by 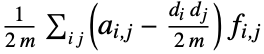 , where
, where 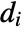 is the out-degree for the vertex vi.
is the out-degree for the vertex vi. - GraphAssortativity works with undirected graphs, directed graphs, weighted graphs, multigraphs, and mixed graphs.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (12)
GraphAssortativity works with undirected graphs:
Use rules to specify the graph:
Compute the assortativity coefficient using vertex property data:
A partition or assignment of a subset of VertexList:
GraphAssortativity works with symbolic expressions:
GraphAssortativity works with large graphs:
Applications (3)
Compare the assortativity coefficient of vertex partitions by vertex color:
Disassortativity by number of friends in a friendship network:
A partition of the network shows assortative mixing:
A friendship network at a high school, with vertices color coded by race. Analyze the preference for students to associate with others who are similar:
Highly social students are friends with other highly social students:
Positive tendency for students to associate with others of the same race:
Properties & Relations (2)
The assortativity coefficient is between -1 and 1:
Completely disassortative graph:
GraphAssortativity is Pearson correlation coefficient of degree between connected vertices:
Correlation gives the Pearson correlation coefficient:
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), GraphAssortativity, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphAssortativity.html (updated 2015).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "GraphAssortativity." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2015. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphAssortativity.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). GraphAssortativity. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphAssortativity.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_graphassortativity, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GraphAssortativity}", year="2015", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphAssortativity.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_graphassortativity, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GraphAssortativity}, year={2015}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphAssortativity.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}