Padding
is an option to various array and image operations that specifies what padding to use when extending beyond the original data specified.
Details

- Padding is typically used in filtering, resizing or spatial transformations, whenever the operation extends beyond the original data domain.
- Typical settings for Padding include:
-
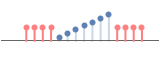
val pad with a constant value val 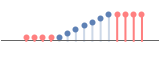
"Fixed" repetitions of the elements on each boundary 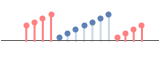
"Periodic" cyclic repetitions of the complete array 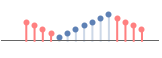
"Reflected" reflections of the array in the boundary 
"Reversed" reversals of the complete array - For a 2D array, "Fixed" indicates that the rectangle of elements added at each corner should be copies of the elements at the corners of the original array.
- "Reversed" indicates that the outermost layer of elements in the array should be repeated as the innermost layer of elements in the padding. "Reflected" specifies that these elements should not be repeated.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (1)
Many filter functions use Padding->"Fixed" to minimize visibility of padding artifacts:
Wolfram Research (2008), Padding, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Padding.html.
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), Padding, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Padding.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "Padding." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Padding.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). Padding. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Padding.html