StateOutputEstimator[ssm,l]
constructs an estimator for the StateSpaceModel ssm, with estimator gain matrix l.
StateOutputEstimator[{ssm,sensors},l]
uses only sensors as the measurements of ssm.
StateOutputEstimator[{ssm,sensors,dinputs},l]
specifies dinputs as the deterministic inputs of ssm.


StateOutputEstimator
StateOutputEstimator[ssm,l]
constructs an estimator for the StateSpaceModel ssm, with estimator gain matrix l.
StateOutputEstimator[{ssm,sensors},l]
uses only sensors as the measurements of ssm.
StateOutputEstimator[{ssm,sensors,dinputs},l]
specifies dinputs as the deterministic inputs of ssm.
Details and Options



- The standard state-space model ssm can be given as StateSpaceModel[{a,b,c,d}], where a, b, c and d represent the state, input, output and transmission matrices in either a continuous-time or a discrete-time system:
-

continuous-time system 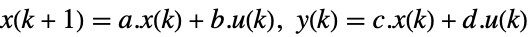
discrete-time system - The descriptor state-space model ssm can be given as StateSpaceModel[{a,b,c,d,e}] in either continuous-time or discrete-time:
-
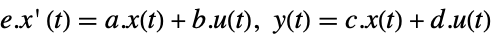
continuous-time system 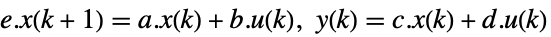
discrete-time system - StateOutputEstimator also accepts nonlinear systems specified by AffineStateSpaceModel and NonlinearStateSpaceModel.
- For nonlinear systems, the operating values of state and input variables are taken into consideration when constructing the estimator.
- The inputs
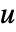 can include stochastic inputs
can include stochastic inputs  and deterministic inputs
and deterministic inputs  .
. - The argument dinputs is a list of integers specifying the positions of
 in
in 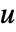 .
. - The outputs
 can include measurements
can include measurements 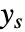 and other outputs.
and other outputs. - The argument sensors is a list of integers specifying the positions of
 in
in 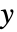 .
. - StateOutputEstimator[ssm,l] is equivalent to StateOutputEstimator[{ssm,All,All},l].
- The estimator gains l can be computed using EstimatorGains, LQEstimatorGains or DiscreteLQEstimatorGains.
- StateOutputEstimator[ssm,LQEstimatorGains[ssm,…],…] gives a Kalman estimator.
- StateOutputEstimator[ssm,EstimatorGains[ssm,…],…] gives a Luenberger estimator.
- StateOutputEstimator supports a Method option. The following explicit settings can be given:
-
"CurrentEstimator" constructs the current estimator "PredictionEstimator" constructs the prediction estimator - The current estimate is based on measurements up to the current instant.
- The prediction estimate is based on measurements up to the previous instant.
- StateOutputEstimator gives an estimator with dynamics
 for continuous-time systems. The matrices with subscripts
for continuous-time systems. The matrices with subscripts  and
and 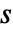 are submatrices associated with the deterministic inputs
are submatrices associated with the deterministic inputs  and the sensors
and the sensors  .
. - The prediction estimator of a discrete-time system has dynamics
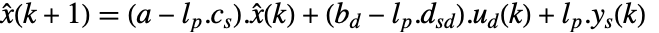 .
. - For discrete-time systems, StateOutputEstimator[…,Method->"CurrentEstimator"] gives an estimator with dynamics
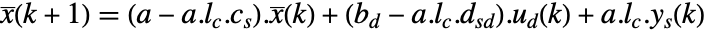 , and the current state estimate
, and the current state estimate  is obtained from the current measurement
is obtained from the current measurement  as
as 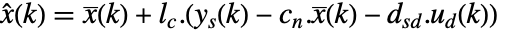 .
. - For discrete-time systems, the prediction gain
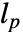 and the current gain
and the current gain 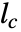 have the relationship
have the relationship  .
. - Block diagram for the system with estimator:
- The inputs to the estimator model are the deterministic inputs
 and the measurements
and the measurements 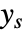 .
. - The outputs of the estimator model consist of the estimated states
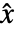 and estimates of the measurements
and estimates of the measurements  .
.

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
The output and state estimator for a continuous-time system:
An estimator of a system with unity estimator gain and a sensor at the second output:
For a discrete-time system, StateOutputEstimator assembles a discrete‐time estimator:
Scope (8)
A linear estimator for a system with one measured output and one deterministic input:
Specify that the input is stochastic:
The estimator for a system in which all the outputs are measured and all inputs are deterministic:
Only the first output is measured:
The first output is measured and the first input is stochastic:
All the outputs are measured and all inputs are stochastic:
An estimator for a descriptor state-space model:
An estimator for an AffineStateSpaceModel:
Compute a set of gains based on the linearized system:
Options (2)
Applications (1)
Properties & Relations (2)
StateOutputEstimator estimates the states and outputs of a system:
Construct a Kalman estimator for a discrete-time system:
Use KalmanEstimator directly:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2010 (8.0) | Updated in 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), StateOutputEstimator, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/StateOutputEstimator.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "StateOutputEstimator." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/StateOutputEstimator.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). StateOutputEstimator. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/StateOutputEstimator.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_stateoutputestimator, author="Wolfram Research", title="{StateOutputEstimator}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/StateOutputEstimator.html}", note=[Accessed: 08-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_stateoutputestimator, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={StateOutputEstimator}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/StateOutputEstimator.html}, note=[Accessed: 08-March-2026]}