Defining Your Own Wavelet
Defining Your Own Wavelet
You can define wavelets to plug into the wavelet analysis framework by using the correct template. A wavelet wave is of the form wfam[args], where wfam is the symbol that indicates the wavelet family and args provide any necessary specification.
In order to set wfam as a wavelet family recognized by the system, the property wfam[patt]["WaveletQ"] must be set to True, where patt is a pattern that matches acceptable arguments args.
| WaveletQ | set to True if the symbol is a user wavelet |
Both orthogonal and biorthogonal user wavelets are supported. Orthogonal wavelets are indicated by setting the property wfam[args]["OrthogonalQ"] and, correspondingly, biorthogonal wavelets are set using the property wfam[args]["BiorthogonalQ"].
| "OrthogonalQ" | set to True if the wavelet is orthogonal |
| "BiorthogonalQ" | set to True if the wavelet is biorthogonal |
To compute primal lowpass filter coefficients, the property wfam[args]["PrimalLowpass",prec] must be set; here prec indicates the precision of filter coefficients. Similarly, to compute dual lowpass filter coefficients, the property "DualLowpass" must be set. Both properties "PrimalLowpass" and "DualLowpass" are expected to return a list of the form 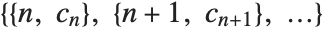 , where
, where 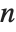 is the index and
is the index and  is the corresponding filter coefficient. If a list of the form
is the corresponding filter coefficient. If a list of the form 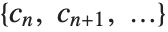 is returned, it is assumed that index
is returned, it is assumed that index 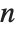 starts from 0. An error message is generated if the filter coefficients
starts from 0. An error message is generated if the filter coefficients  are not numeric and indices
are not numeric and indices 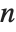 are not integers.
are not integers.
Franklin Wavelet
The scaling function is computed using the recursive equation 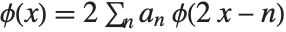 , where
, where 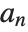 represents the lowpass filter coefficients.
represents the lowpass filter coefficients.
Legendre Wavelet
Although Legendre wavelets are not orthogonal, to be able to perform a wavelet transform, you need to set it to True:
The wavelet function is computed using the recursive equation 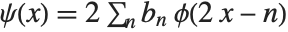 , where
, where 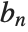 represents the highpass filter coefficients.
represents the highpass filter coefficients.
Le Gall Wavelet
Perform a StationaryWaveletTransform using a Le Gall wavelet: