WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
RheostatMotorControlMotor controlled by a thumbwheel potentiometer in rheostat configuration |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.ElectricalEngineering.Potentiometers.RheostatMotorControl"]
Information
Potentiometers, also knows as pots, are useful electrical components that allows a person or a machine to directly tune the voltage or restiance in one part of a circuit. In its normal configuration, a potentiometer acts as a variable voltage divider. If a voltage source is connected between the two pins called terminals, the voltage over the third pin, known as the wiper will vary with the position of the potentiometer shaft. This shaft can for example be controlled by a slider or a thumbwheel.
Model
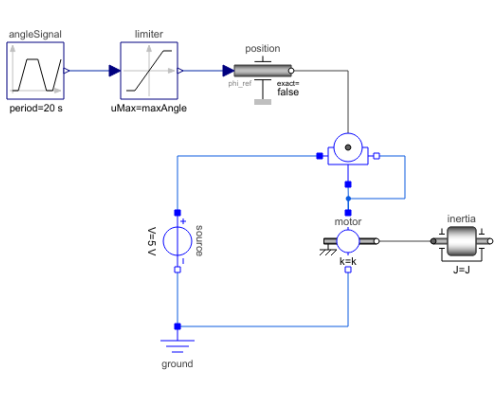
In this example model, a thumbwheel potentiometer has been connected in a rheostat configuration, working as a variable resistor. The terminal pin connected to the ground has been short-circuited with the wiper pin. This means that the voltage over the terminal to the wiper will be the same as over the two terminals. The rheostat has been connected in a series with a motor. The motor in turn drives a body with inertia.
The torque produced by the motor will be proportional to the current running through the motor. Since the motor is connected in a series with the potentiometer, the current throught the motor will be the same as the current through the potentiometer. By turning the potentiometer the motor torque can be controlled.
Simulation
To simulate the model, click the Simulate button:
Plot the results
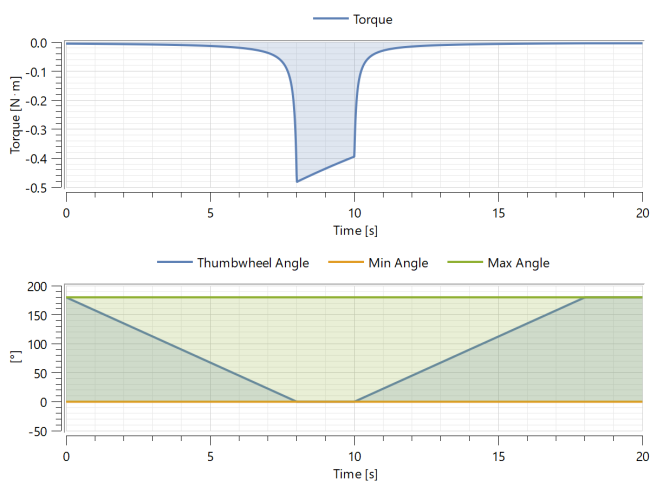
Explore how the torque from the motor increases as the thumbwheel is turned. Plot the Model plot called Motor torque by double clicking it from the Model Plots section.
You should now see the graph below:
Parameters (6)
| minAngle |
Value: 0 Type: Angle (rad) Description: Minimum angle for the thumbwheel. |
|---|---|
| maxAngle |
Value: 3.14159265358979 Type: Angle (rad) Description: Maximum angle for the thumbwheel. |
| minRes |
Value: 10 Type: Resistance (Ω) Description: Minimum resistance for the potentiometer. |
| maxRes |
Value: 1000 Type: Resistance (Ω) Description: Maximum resistance for the potentiometer. |
| J |
Value: 1 Type: Inertia (kg⋅m²) Description: Inertia of the body driven by the motor. |
| k |
Value: 1 Type: ElectricalTorqueConstant (N⋅m/A) Description: Transformation coeffiecient of the motor. |
Components (8)
| potentionmeter |
Type: ThumbwheelPotentiometer Description: Thumbwheel potentiometer in rheostat configuration. |
|
|---|---|---|
| ground |
Type: Ground Description: Ground component. |
|
| position |
Type: Position Description: Angle of the thumbwheel potentiometer. |
|
| source |
Type: ConstantVoltage Description: Constant voltage source. |
|
| angleSignal |
Type: Trapezoid Description: Trapezoid signal that sets the angle of the thumbwheel potentiometer. |
|
| motor |
Type: RotationalEMF Description: Motor controlled by rheostat. |
|
| inertia |
Type: Inertia Description: Motor inertia. |
|
| limiter |
Type: Limiter Description: Limit the range of a signal |