WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
RoughPipeSegmentModel of flow through a pipe |
|
Wolfram Language
In[1]:=
SystemModel["Hydraulic.Restrictions.Pipes.Internal.RoughPipeSegment"]
Out[1]:=

Information
This class models the pressure loss for a pipe. For the pipe flow, we assume that the pipe diameter D stays constant and that the pipe is straight. The energy equation for a non-horizontal pipe gives us the following equation:
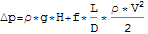
The friction f can be computed from the Reynolds number according to the Colebrook equation below:
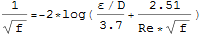
where
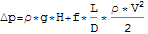
The friction f can be computed from the Reynolds number according to the Colebrook equation below:
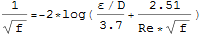
where
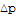 | : | Pressure difference between ports a and b | |
 | : | Fluid density | |
| g | : | Standard acceleration of gravity on Earth | |
| H | : | Height difference between ports a and b | |
| f | : | Pipe friction | |
| L | : | Pipe length | |
| D | : | Inner pipe diameter | |
| V | : | Fluid velocity | |
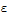 | : | Pipe roughness |
Reference
F. Young, R. Munson, H. Okiishi, and W. Huebsch, A Brief Introduction to Fluid Mechanics, 4th ed., Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2007 p. 291.Parameters (5)
| medium |
Value: Oil() Type: Medium Description: Medium in the component |
|---|---|
| D |
Value: 0.1 Type: Diameter (m) Description: Inner pipe diameter |
| L |
Value: 1 Type: Length (m) Description: Pipe length |
| H |
Value: 0 Type: Length (m) Description: Height for point B minus height for point A |
| epsilon |
Value: 0.00026 Type: Real Description: Pipe roughness |
Connectors (2)
Components (1)
| medium |
Type: Medium Description: Medium in the component |
|---|
