WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
GlycolysisModelMain model - Extracellular compartment |
|
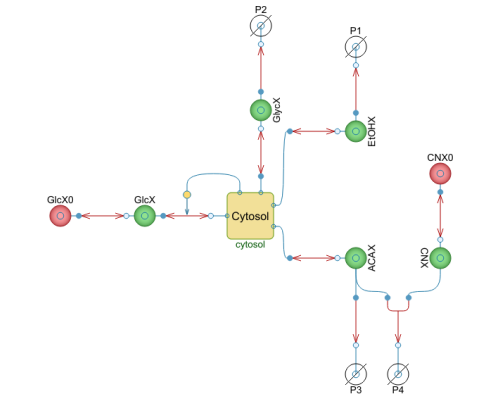
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["IndustryExamples.LifeSciences.Glycolysis.GlycolysisModel"]
Information
Library Dependency
This model requires the BioChem library.
- The free BioChem library is an extendable, general purpose Modelica library for modeling, simulation and visualization of biological and biochemical systems. The library is designed to be used together with Wolfram System Modeler, which enables several extra features such as Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML) import and export. BioChem can, for instance, be used for selecting drug targets with PK/PD modeling or searching for novel drug targets with mechanistic modeling of the reactions in a cell or organism.
Model
This is the main model in this example, and it simulates glycolytic oscillations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast cells) as described in F. Hynne, S. Danø, and P. G. Sørensen, "Full-Scale Model of Glycolysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae," Biophysical Chemistry, 94(1–2), 2001 pp. 121–163.
The model has been imported from the BioModels Database using the SBML importer in Wolfram System Modeler and designed using the BioChem library.
To import SBML models in Wolfram System Modeler, the Systems Biology add-on needs to be enabled. To enable this add-on, open the options dialog box by choosing Tools ▶ Options. The setting is located in the Global ▶ Add-On Products view. Note that for the changes to have an effect after changing this setting, System Modeler must be restarted.
More information on the Systems Biology add-on can be found under Help ▶ Systems Biology.
View the model diagram for this model.
Simulation
Simulate the model by clicking the Simulate button:
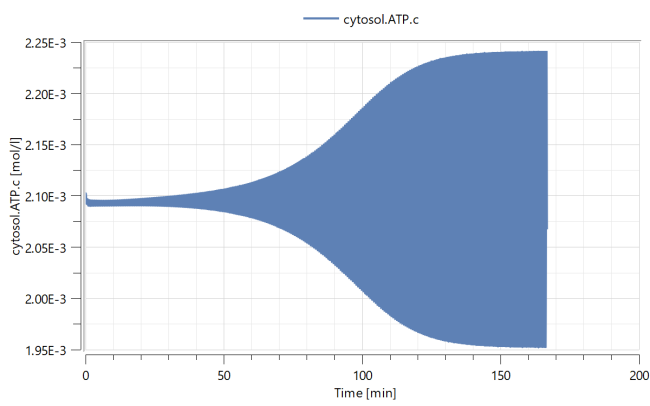
In its default configuration, the model produces a stable limit cycle. Look at, for instance, the variable cytosol.ATP.c to study the oscillations. Plot the variable by expanding the tree in the Plot view in the Simulation Center. First expand the cytosol branch, then the ATP branch, and finally select the c variable by checking the box next to it.
The plot of the variable will appear in a plot window to the right.
To simulate the model on the other side of the bifurcation point, update the initial conditions of the model by choosing Tools ▶ Initialize ▶ From Experiment. This sets the initial state for the next simulation to be the final state of the previous simulation.
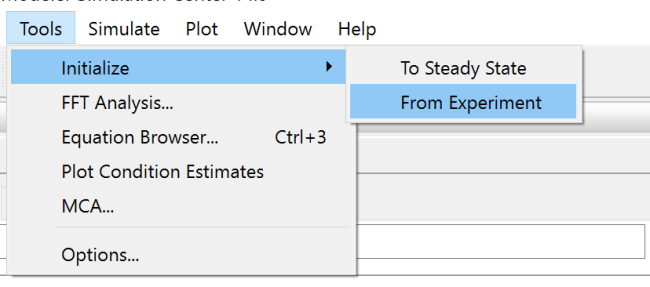
Select your current experiment, for instance GlycolysisModel 1, and click OK.
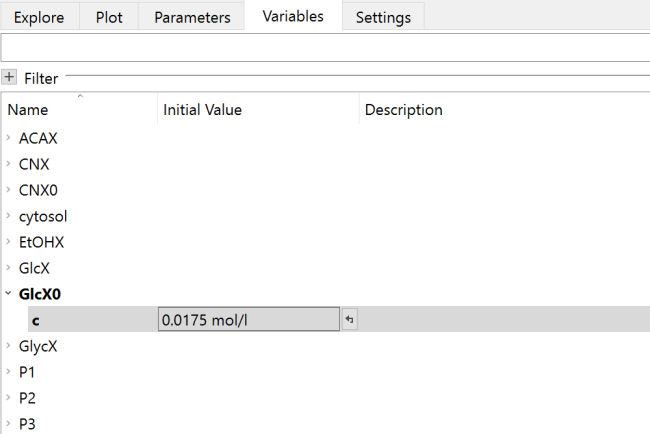
Finally, change the initial value of GlcX0.c from 0.020 to 0.0175 in the Variables tab in Simulation Center.
Simulating again, the variable cytosol.ATP.c will now converge back to a steady state.
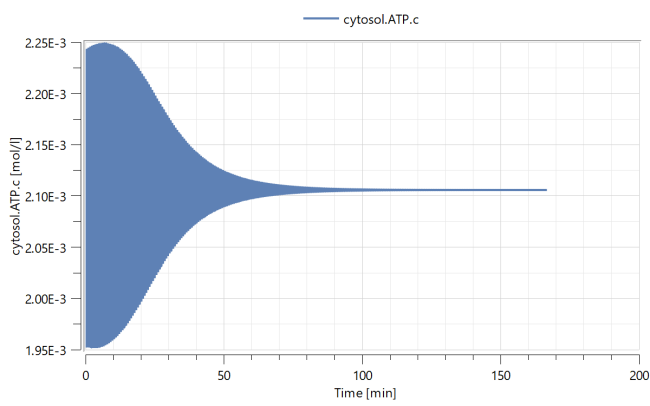
As you can see, small changes in a bifurcation parameter can qualitatively change the oscillations of protein and molecule concentrations.
Parameters (1)
| mainCompartment |
Value: true Type: Boolean Description: Specifies whether the compartment is a main (top-level) compartment. Used in SBML import/export. |
|---|
Components (22)
| cytosol |
Type: Cytosol Description: Cytosolic compartment |
|
|---|---|---|
| GlcX |
Type: GlcX_ Description: Extracellular glucose |
|
| EtOHX |
Type: EtOHX_ Description: Extracellular ethanol |
|
| GlycX |
Type: GlycX_ Description: Extracellular glycerol |
|
| ACAX |
Type: ACAX_ Description: Extracellular acetaldehyde |
|
| CNX |
Type: CNX_ Description: Extracellular cyanide |
|
| CNX0 |
Type: CNX0_ Description: Mixed flow cyanide |
|
| GlcX0 |
Type: GlcX0_ Description: Mixed flow glucose |
|
| vinGlc |
Type: vinGlc_ Description: Glucose Mixed flow to extracellular medium |
|
| vGlcTrans |
Type: vGlcTrans_ Description: Glucose uptake |
|
| vdifEtOH |
Type: vdifEtOH_ Description: Ethanol out |
|
| voutEtOH |
Type: voutEtOH_ Description: Ethanol flow |
|
| vdifGlyc |
Type: vdifGlyc_ Description: Glycerol out |
|
| voutGlyc |
Type: voutGlyc_ Description: Glycerol flow |
|
| vdifACA |
Type: vdifACA_ Description: Acetaldehyde out |
|
| voutACA |
Type: voutACA_ Description: Acetaldehyde flow |
|
| vlacto |
Type: vlacto_ Description: Cyanide-Acetaldehyde flow |
|
| vinCN |
Type: vinCN_ Description: Cyanide flow |
|
| P1 |
Type: AmbientSubstance Description: Substance used as a reservoir in reactions |
|
| P2 |
Type: AmbientSubstance Description: Substance used as a reservoir in reactions |
|
| P3 |
Type: AmbientSubstance Description: Substance used as a reservoir in reactions |
|
| P4 |
Type: AmbientSubstance Description: Substance used as a reservoir in reactions |