WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
GenerationOfFMUsExample to demonstrate variants to generate FMUs (Functional Mock-up Units) |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.Examples.GenerationOfFMUs"]
Information
This information is part of the Modelica Standard Library maintained by the Modelica Association.
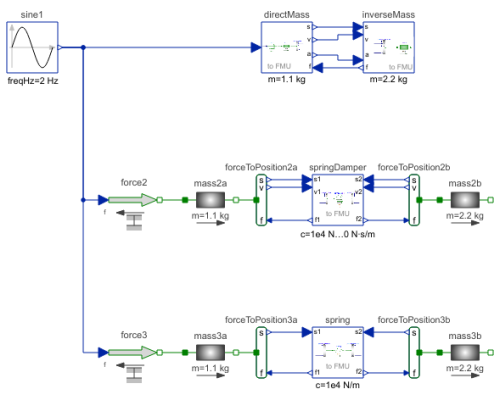
This example demonstrates how to generate an input/output block (e.g. in form of an FMU - Functional Mock-up Unit) from various Translational components. The goal is to export such an input/output block from Modelica and import it in another modeling environment. The essential issue is that before exporting it must be known in which way the component is utilized in the target environment. Depending on the target usage, different flange variables need to be in the interface with either input or output causality. Note, this example model can be used to test the FMU export/import of a Modelica tool. Just export the components marked in the icons as "toFMU" as FMUs and import them back. The models should then still work and give the same results as a pure Modelica model.
Connecting two masses
The upper part (DirectMass, InverseMass)
demonstrates how to export two masses and connect them
together in a target system. This requires that one of the masses
(here: DirectMass)
is defined to have states and the position, velocity and
acceleration are provided in the interface.
The other mass (here: InverseMass) is moved according
to the provided input position, velocity and acceleration.
Connecting a force element that needs position and velocities
The middle part (SpringDamper) demonstrates how to export a force element
that needs both position and velocities for its force law and connect this
force law in a target system between two masses.
Connecting a force element that needs only positions
The lower part (Spring) demonstrates how to export a force element
that needs only positions for its force law and connect this
force law in a target system between two masses.
Components (15)
| sine1 |
Type: Sine |
|
|---|---|---|
| directMass |
Type: DirectMass |
|
| inverseMass |
Type: InverseMass |
|
| springDamper |
Type: SpringDamper |
|
| mass2a |
Type: Mass |
|
| force2 |
Type: Force |
|
| forceToPosition2a | ||
| mass2b |
Type: Mass |
|
| forceToPosition2b | ||
| spring |
Type: Spring |
|
| mass3a |
Type: Mass |
|
| force3 |
Type: Force |
|
| forceToPosition3a | ||
| mass3b |
Type: Mass |
|
| forceToPosition3b |