ParallelTable[expr,{imax}]
generates in parallel a list of imax copies of expr.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imax}]
generates in parallel a list of the values of expr when i runs from 1 to imax.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax}]
starts with i=imin.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax,di}]
uses steps di.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,{i1,i2,…}}]
uses the successive values i1, i2, ….
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax},{j,jmin,jmax},…]
gives a nested list. The list associated with i is outermost.


ParallelTable
ParallelTable[expr,{imax}]
generates in parallel a list of imax copies of expr.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imax}]
generates in parallel a list of the values of expr when i runs from 1 to imax.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax}]
starts with i=imin.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax,di}]
uses steps di.
ParallelTable[expr,{i,{i1,i2,…}}]
uses the successive values i1, i2, ….
ParallelTable[expr,{i,imin,imax},{j,jmin,jmax},…]
gives a nested list. The list associated with i is outermost.
Details and Options


- ParallelTable is a parallel version of Table that automatically distributes different evaluations of expr among different kernels and processors.
- ParallelTable will give the same results as Table, except for side effects during the computation.
- Parallelize[Table[expr,iter, …]] is equivalent to ParallelTable[expr,iter,…].
- If an instance of ParallelTable cannot be parallelized, it is evaluated using Table.
- The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic granularity of parallelization DistributedContexts $DistributedContexts contexts used to distribute symbols to parallel computations ProgressReporting $ProgressReporting whether to report the progress of the computation - The Method option specifies the parallelization method to use. Possible settings include:
-
"CoarsestGrained" break the computation into as many pieces as there are available kernels "FinestGrained" break the computation into the smallest possible subunits "EvaluationsPerKernel"->e break the computation into at most e pieces per kernel "ItemsPerEvaluation"->m break the computation into evaluations of at most m subunits each Automatic compromise between overhead and load balancing - Method->"CoarsestGrained" is suitable for computations involving many subunits, all of which take the same amount of time. It minimizes overhead, but does not provide any load balancing.
- Method->"FinestGrained" is suitable for computations involving few subunits whose evaluations take different amounts of time. It leads to higher overhead, but maximizes load balancing.
- By default, a nested table with a large outermost level is parallelized at the outermost level, otherwise, at the innermost level. With Method->"CoarsestGrained", it is parallelized at the outermost level. With Method->"FinestGrained", it is parallelized at the innermost level.
- The DistributedContexts option specifies which symbols appearing in expr have their definitions automatically distributed to all available kernels before the computation.
- The default value is DistributedContexts:>$DistributedContexts with $DistributedContexts:=$Context, which distributes definitions of all symbols in the current context but does not distribute definitions of symbols from packages.
- The ProgressReporting option specifies whether to report the progress of the parallel computation.
- The default value is ProgressReporting:>$ProgressReporting.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
ParallelTable works like Table, but in parallel:
A table of the first 10 squares:
A table with i running from 0 to 20 in steps of 2:
Longer computations display information about their progress and estimated time to completion:
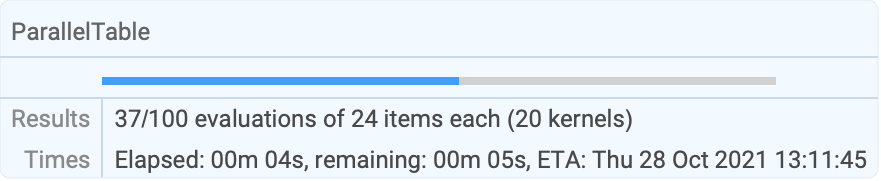
| |
Scope (5)
Options (14)
Method (7)
Break the computation into the smallest possible subunits:
Break the computation into as many pieces as there are available kernels:
Break the computation into at most 2 evaluations per kernel for the entire job:
Break the computation into evaluations of at most 5 elements each:
The default option setting balances evaluation size and number of evaluations:
Calculations with vastly differing runtimes should be parallelized as finely as possible:
A large number of simple calculations should be distributed into as few batches as possible:
By default, a small nested table is parallelized fully at the innermost level:
To parallelize only at the first level, use Method"CoarsestGrained":
DistributedContexts (5)
By default, definitions in the current context are distributed automatically:
Do not distribute any definitions of functions:
Distribute definitions for all symbols in all contexts appearing in a parallel computation:
Distribute only definitions in the given contexts:
Restore the value of the DistributedContexts option to its default:
ProgressReporting (2)
Do not show a temporary progress report:
Use Method"FinestGrained" for the most accurate progress report:
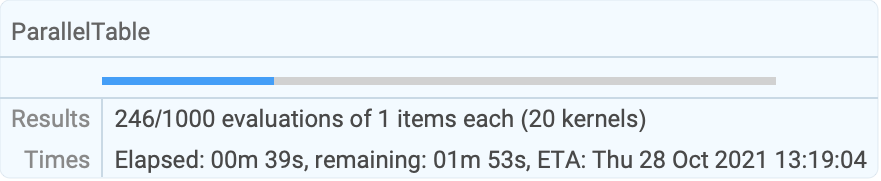
| |
Applications (5)
Solve and plot a differential equation for many initial conditions and animate the results:
Explore different parameter values for the sine-Gordon equation in two spatial dimensions:
Apply different algorithms to the same set of data:
Apply a list of different filters to the same image and display the result:
Generate 10 frames from an animation and save them to individual files:
Run several batches in parallel:
Each run returns one frame which can be used for checking the correctness:
Quickly show the evaluation of several nontrivial cellular automata:
Properties & Relations (10)
Parallelization happens along the outermost (first) index:
Using multiple iteration specifications is equivalent to nesting Table functions:
ParallelDo evaluates the same sequence of expressions as ParallelTable:
ParallelSum effectively applies Plus to results from ParallelTable:
ParallelArray iterates over successive integers:
Map applies a function to successive elements in a list:
Table can substitute successive elements in a list into an expression:
ParallelTable iterating over a given list is equivalent to ParallelCombine:
ParallelTable can be implemented with WaitAll and ParallelSubmit:
Parallelization at the innermost level of a multidimensional table:
Functions defined interactively are automatically distributed to all kernels when needed:
Distribute definitions manually and disable automatic distribution:
For functions from a package, use ParallelNeeds rather than DistributeDefinitions:
Possible Issues (3)
A function used that is not known on the parallel kernels may lead to sequential evaluation:
Define the function on all parallel kernels:
The function is now evaluated on the parallel kernels:
Definitions of functions in the current context are distributed automatically:
Definitions from contexts other than the default context are not distributed automatically:
Use DistributeDefinitions to distribute such definitions:
Alternatively, set the DistributedContexts option to include all contexts:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2008 (7.0) | Updated in 2010 (8.0) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), ParallelTable, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelTable.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "ParallelTable." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelTable.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). ParallelTable. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelTable.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_paralleltable, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ParallelTable}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelTable.html}", note=[Accessed: 31-August-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_paralleltable, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ParallelTable}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelTable.html}, note=[Accessed: 31-August-2025]}