Inpaint[image,region]
retouches parts of image that correspond to nonzero elements in region.


Inpaint
Inpaint[image,region]
retouches parts of image that correspond to nonzero elements in region.
Details and Options


- Image inpainting, also known as retouching, is the process of synthesizing new pixels for regions of an image. It is typically used to recover damage, remove unwanted content or create new content.
- Inpaint works with arbitrary 2D images, operating separately on each channel.
- The region to be retouched can be given as an image, a graphics object, or a matrix.
- The region specification can be any of the following:
-
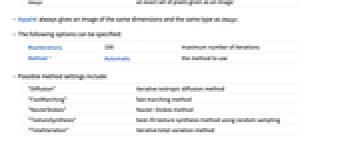
pos region computed as the component specified by {x,y} {pos1,pos2,…} region containing all posi Rectangle[…] region indicated by a bounding box image an exact set of pixels given as an image - Inpaint always gives an image of the same dimensions and the same type as image.
- The following options can be specified:
-
MaxIterations 100 maximum number of iterations Method Automatic the method to use - Possible method settings include:
-
"Diffusion" iterative isotropic diffusion method "FastMarching" fast marching method "NavierStokes" Navier–Stokes method "TextureSynthesis" best-fit texture synthesis method using random sampling "TotalVariation" iterative total variation method - By default, the "TextureSynthesis" method is used.
- Inpaint operates separately on each color channel, except for the "TextureSynthesis" method.
- With Method->{"TotalVariation",subopt}, the following suboptions can be specified:
-
"NoiseModel" "Gaussian" "Gaussian", "Laplacian", or "Poisson" "Regularization" Automatic regularization parameter - With Method->{"TextureSynthesis",subopt}, the following suboptions can be specified:
-
Masking Automatic binary mask specifying the pixels to use in finding a best-fit texture "MaxSamples" 300 maximum number of samples used to find the best-fit texture "NeighborCount" 30 number of nearby pixels used for texture comparison

Examples
open all close allScope (4)
Options (3)
Applications (7)
Properties & Relations (1)
History
Introduced in 2010 (8.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2015 (10.2) ▪ 2024 (14.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), Inpaint, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inpaint.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "Inpaint." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inpaint.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). Inpaint. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inpaint.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_inpaint, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Inpaint}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inpaint.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_inpaint, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Inpaint}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inpaint.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}