HexahedronElement[{{i11,…,i18},…,{in1,…,in8}}]
represents n linear hexahedron elements ek with incidents {ik1,…ik8}.
HexahedronElement[{{i11,…,i120},…,{in1,…,in20}}]
represents n quadratic hexahedron elements ek with incidents {ik1,…,ik20}.
HexahedronElement[{e1,…,en},{m1,…,mn}]
represents n hexahedron elements ek and n integer markers mk.


HexahedronElement
HexahedronElement[{{i11,…,i18},…,{in1,…,in8}}]
represents n linear hexahedron elements ek with incidents {ik1,…ik8}.
HexahedronElement[{{i11,…,i120},…,{in1,…,in20}}]
represents n quadratic hexahedron elements ek with incidents {ik1,…,ik20}.
HexahedronElement[{e1,…,en},{m1,…,mn}]
represents n hexahedron elements ek and n integer markers mk.
Details and Options
- HexahedronElement is used to represent hexahedron mesh elements in ElementMesh.
- HexahedronElement can be used as an input to ToElementMesh or ToBoundaryMesh.
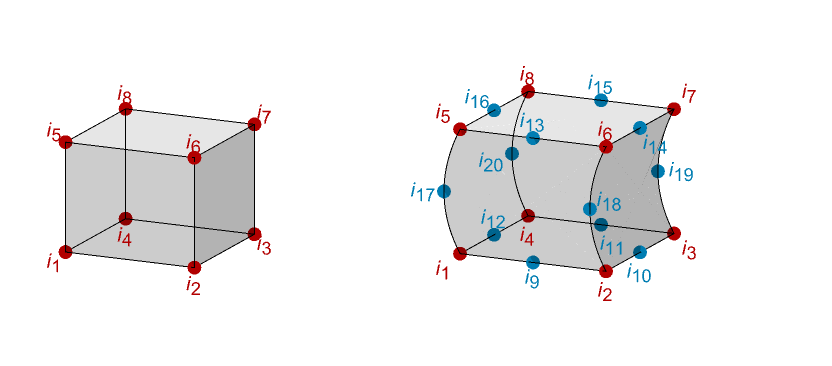
- Incidents ik,j are integers that index an array of spatial coordinates. The coordinates referenced by ek={ik1,…} are the nodes of the k
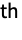 triangle.
triangle. - The first three incidents ik1 until ik8 are always vertices.
- For quadratic triangle elements, the next 12 incidents are mid-side nodes of possibly curved edges.
- Linear elements are order 1 elements and quadratic elements are order 2 elements.
- In HexahedronElement[{e1,…,en}], all elements ek need to be of the same order.
- The hexahedra in HexahedronElement[{e1,…,en}] will share common nodes, edges, and faces, but cannot intersect with each other or with themselves.
- The nodes for a linear and a quadratic hexahedron are shown:
- For a HexahedronElement, the incidents on the faces must be counterclockwise when viewed from inside the element. An element {i1,…,i8} has face incidents {i1,i2,i3,i4}, {i8,i7,i6,i5}, {i1,i5,i6,i2}, {i2,i6,i7,i3}, {i3,i7,i8,i4}, and {i4,i8,i5,i1} for the six faces.
- The hexahedron element is known in the finite element method as a Serendipity element.
Examples
open all close allGeneralizations & Extensions (4)
The base coordinates of the linear element:
The base incidents of the linear element:
A mesh with a linear unit element:
Visualization of the linear unit element:
The base coordinates of the quadratic element:
The base incidents of the quadratic element:
Applications (1)
Possible Issues (6)
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), HexahedronElement, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/FEMDocumentation/ref/HexahedronElement.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "HexahedronElement." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/FEMDocumentation/ref/HexahedronElement.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). HexahedronElement. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/FEMDocumentation/ref/HexahedronElement.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hexahedronelement, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HexahedronElement}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/FEMDocumentation/ref/HexahedronElement.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hexahedronelement, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HexahedronElement}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/FEMDocumentation/ref/HexahedronElement.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}