NFourierCoefficient[expr,t,n]
gives a numerical approximation to the n![]() coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr, where expr is a periodic function of t with period 2π.
coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr, where expr is a periodic function of t with period 2π.
Details and Options


Examples
Basic Examples
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
FourierSeries`
FourierSeries`
NFourierCoefficient
NFourierCoefficient[expr,t,n]
gives a numerical approximation to the n![]() coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr, where expr is a periodic function of t with period 2π.
coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr, where expr is a periodic function of t with period 2π.
Details and Options
- To use NFourierCoefficient, you first need to load the Fourier Series Package using Needs["FourierSeries`"].
- The numerical approximation to the n
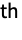 coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr is by default defined to be
coefficient in the Fourier exponential series expansion of expr is by default defined to be 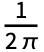 NIntegrate[expr -nt,{t,-π,π}], where n must be an integer.
NIntegrate[expr -nt,{t,-π,π}], where n must be an integer. - Different choices for the definition of the Fourier exponential series expansion can be specified using the option FourierParameters.
- With the setting FourierParameters->{a,b}, expr is assumed to have a period of
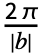 , and the n
, and the n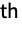 coefficient computed by NFourierCoefficient is
coefficient computed by NFourierCoefficient is 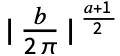 NIntegrate[expr -bnt,{t,-
NIntegrate[expr -bnt,{t,-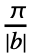 ,
,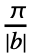 }].
}]. - The parameter b in the setting FourierParameters->{a,b} must be numeric.
- In addition to the option FourierParameters, NFourierCoefficient can also accept the options available to NIntegrate. These options are passed directly to NIntegrate.