is an option for various numerical operations which specifies how many effective digits of accuracy should be sought in the final result.


AccuracyGoal
is an option for various numerical operations which specifies how many effective digits of accuracy should be sought in the final result.
Details

- AccuracyGoal is an option for such functions as NIntegrate, NDSolve, and FindRoot.
- AccuracyGoal->Automatic normally yields an accuracy goal equal to half the setting for WorkingPrecision.
- AccuracyGoal->Infinity specifies that accuracy should not be used as the criterion for terminating the numerical procedure. PrecisionGoal is typically used in this case.
- Even though you may specify AccuracyGoal->n, the results you get may sometimes have much less than n‐digit accuracy.
- In most cases, you must set WorkingPrecision to be at least as large as AccuracyGoal.
- AccuracyGoal effectively specifies the absolute error allowed in a numerical procedure.
- With AccuracyGoal->a and PrecisionGoal->p, the Wolfram Language attempts to make the numerical error in a result of size
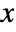 be less than
be less than 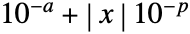 .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Approximate a numerical integral to at least 8 digits of accuracy:
Use precision (relative error) as the basis for error control in solving an ODE:
Without specifying the AccuracyGoal, the relative error is much larger:
Scope (2)
Find a minimum with convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Use convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Use convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() not possible at machine precision:
not possible at machine precision:
Use a higher working precision to allow convergence:
Solve a differential equation using high-precision arithmetic:
Use AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal at half the 32-digit working precision:
This corresponds to the automatic setting used by NDSolve:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2003 (5.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), AccuracyGoal, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AccuracyGoal.html (updated 2003).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "AccuracyGoal." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2003. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AccuracyGoal.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). AccuracyGoal. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AccuracyGoal.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_accuracygoal, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AccuracyGoal}", year="2003", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AccuracyGoal.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_accuracygoal, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AccuracyGoal}, year={2003}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AccuracyGoal.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}