CyclicGroup[n]
represents the cyclic group of degree n.


CyclicGroup
CyclicGroup[n]
represents the cyclic group of degree n.
Details
- The degree n of CyclicGroup[n] must be a non-negative integer. Degrees 0 and 1 correspond to the trivial or identity group.
- CyclicGroup[n] is represented by default as a permutation group on the points {1,…,n}.
- Cyclic groups are commutative.
Background & Context
- CyclicGroup[n] represents the cyclic group
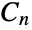 of order n (also denoted
of order n (also denoted 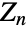 ,
, 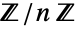 ,
, 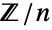 or
or 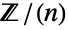 ) for a given non-negative integer n. For
) for a given non-negative integer n. For 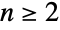 , the default representation of CyclicGroup[n] is as a permutation group on the symbols
, the default representation of CyclicGroup[n] is as a permutation group on the symbols  . The special cases CyclicGroup[0] and CyclicGroup[1] are equivalent to the trivial group with exactly one element.
. The special cases CyclicGroup[0] and CyclicGroup[1] are equivalent to the trivial group with exactly one element. - Mathematically, a cyclic group is a group
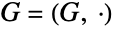 containing an element
containing an element 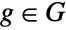 known as a generator, such that every element
known as a generator, such that every element 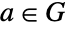 can be written in the form
can be written in the form 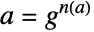 for some non-negative integer
for some non-negative integer 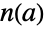 less than the order of
less than the order of 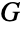 . It follows immediately that any such
. It follows immediately that any such 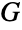 is Abelian (i.e. commutative), since
is Abelian (i.e. commutative), since 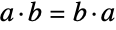 for all elements
for all elements 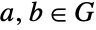 . If
. If 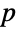 is a prime number, any group with
is a prime number, any group with 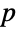 elements is isomorphic to CyclicGroup[p], and by the fundamental theorem of finite Abelian groups, every Abelian group
elements is isomorphic to CyclicGroup[p], and by the fundamental theorem of finite Abelian groups, every Abelian group 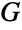 having a finite number of elements can be expressed as a direct product
having a finite number of elements can be expressed as a direct product 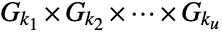 , where Gki=CyclicGroup[ki] and each ki is a power of a prime number. Cyclic groups are permutation groups.
, where Gki=CyclicGroup[ki] and each ki is a power of a prime number. Cyclic groups are permutation groups. - The usual group theoretic functions may be applied to CyclicGroup[n], including GroupOrder, GroupGenerators, GroupElements and so on. A number of precomputed properties of the cyclic group
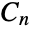 are available via FiniteGroupData[{"CyclicGroup",n},"prop"].
are available via FiniteGroupData[{"CyclicGroup",n},"prop"]. - The class of cyclic groups serves as the basis for a number of related generalizations including virtually cyclic groups, locally cyclic groups and polycyclic groups, many of which are of fundamental importance in abstract algebra, number theory, geometric group theory and topology.
- Other infinite families of finite groups built into the Wolfram Language that are parametrized by integers include AbelianGroup, AlternatingGroup, DihedralGroup and SymmetricGroup.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (1)
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), CyclicGroup, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CyclicGroup.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "CyclicGroup." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CyclicGroup.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). CyclicGroup. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CyclicGroup.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_cyclicgroup, author="Wolfram Research", title="{CyclicGroup}", year="2010", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CyclicGroup.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_cyclicgroup, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={CyclicGroup}, year={2010}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CyclicGroup.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}