Divisible
Details

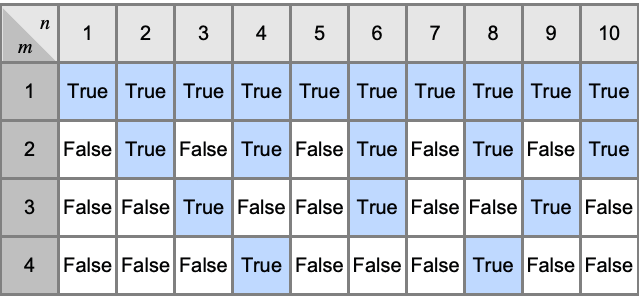
- Divisible is typically used to test whether n is divisible by m.
- n is divisible by m if n is the product of m by an integer.
- Divisible[n,m] is effectively equivalent to Mod[n,m]==0.
- Divisible[n, m] returns False unless n and m are manifestly divisible.
- Divisible[n,m] can be entered as
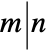 .
.  can be entered as \[Divides] or
can be entered as \[Divides] or  divides
divides .
.
Examples
open all close allScope (6)
Divisible works over integers:
Symbolic forms of numeric quantities:
Divisible threads elementwise over lists:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (8)
Basic Applications (3)
Number Theory (5)
Recognize Wieferich primes, prime numbers p such that ![]() divides
divides ![]() :
:
There are only two known Wieferich primes:
Let ![]() be all numbers of the form
be all numbers of the form ![]() :
:
Check that the product of two numbers is still in ![]() :
:
Recognize Hilbert primes, prime numbers that have no divisors in ![]() other than
other than ![]() and themself:
and themself:
Find the first ![]() Hilbert primes:
Hilbert primes:
Find two representations of a number as the sum of two squares:
Find a divisor of the number by computing the GCD of ![]() and the number:
and the number:
Find another divisor by computing the GCD of ![]() and the number:
and the number:
An integer is divisible by ![]() if the sum of its digits is divisible by
if the sum of its digits is divisible by ![]() :
:
An integer is divisible by ![]() if the alternating sum of the digits is divisible by
if the alternating sum of the digits is divisible by ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (7)
If ![]() is an integer, then
is an integer, then ![]() is divisible by
is divisible by ![]() :
:
If ![]() is divisible by
is divisible by ![]() , then the greatest common divisor GCD of them is
, then the greatest common divisor GCD of them is ![]() :
:
If ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime, then
are relatively prime, then ![]() is not divisible by
is not divisible by ![]() :
:
If the prime factorization of an integer has the form ![]() , then the number of its divisors is
, then the number of its divisors is ![]() :
:
Use Divisors to find all divisors of an integer:
PrimeNu gives the number of distinct prime divisors:
Possible Issues (2)
Interactive Examples (1)
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), Divisible, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Divisible.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "Divisible." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Divisible.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). Divisible. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Divisible.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_divisible, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Divisible}", year="2007", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Divisible.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_divisible, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Divisible}, year={2007}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Divisible.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}

