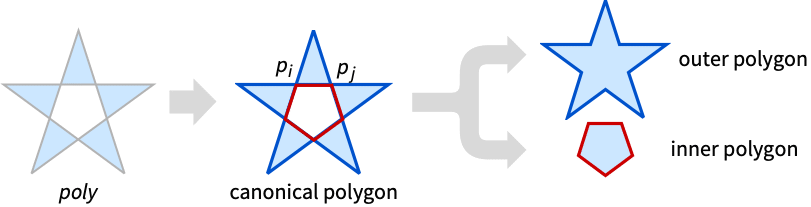
InnerPolygon[poly]
gives the inner polygon of the polygon poly.


InnerPolygon
InnerPolygon[poly]
gives the inner polygon of the polygon poly.
Details

- InnerPolygon is also known as inner ring or hole.
- Typically used to decompose a polygon as a difference of simple polygons, even when the original construction of the polygon was using crossing curves etc.
- InnerPolygon is defined by the canonicalization performed in CanonicalizePolygon.
- InnerPolygon gives a polygon of the form Polygon[{p1,p2,…}, {{i1,i2,…},…}], where pk are explicit coordinates and ik are integer indexes referring to coordinates in the list {p1,p2,…}.
- If poly is a polygon without a hole, then the result is an EmptyRegion object.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Get the inner polygon of a Polygon:
Scope (6)
InnerPolygon works on polygons:
InnerPolygon works on polygons with GeoPosition:
Polygons with GeoGridPosition:
Properties & Relations (1)
InnerPolygon of a simple polygon is an empty polygon:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), InnerPolygon, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InnerPolygon.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "InnerPolygon." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InnerPolygon.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). InnerPolygon. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InnerPolygon.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_innerpolygon, author="Wolfram Research", title="{InnerPolygon}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InnerPolygon.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_innerpolygon, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={InnerPolygon}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InnerPolygon.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}