TagSet 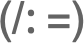
f/:lhs=rhs
assigns rhs to be the value of lhs, and associates the assignment with the symbol f.
Details

- TagSet defines upvalues, downvalues or subvalues as appropriate.
- The symbol f in f/:lhs=rhs must appear in lhs as the head of lhs, the head of the head, one of the elements of lhs, or the head of one of the elements.
- A common case is f/:h[f[args]]=rhs.
- You can see all the rules associated with a particular symbol by typing ?symbol.
- If f appears several times in lhs, then f/:lhs=rhs associates the assignment with each occurrence.
- When it appears in unevaluated symbolic form, TagSet is treated as a scoping construct so that variables in nested occurrences are renamed if necessary.
Examples
open allclose allScope (3)
Properties & Relations (5)
^= defines upvalues in the same way as using a tag does:
The right side of an immediate definition is evaluated when the definition is made:
The right side of a delayed definition is evaluated each time the definition is used:
Definitions with the same left side overwrite earlier ones:
Definition prints definitions associated with a symbol:
Information prints various information about a symbol, including any definitions:
UpValues returns a list of rules corresponding to any upvalues defined:
Use =. to clear definitions with a particular left-hand side:
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), TagSet, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TagSet.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "TagSet." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TagSet.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). TagSet. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TagSet.html