

Tree
Details and Options



- Tree objects represent rooted, ordered, labeled trees with leaves. Standard examples include XML, JSON, file systems and Wolfram Language notebooks and expressions.
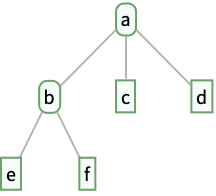
- Tree[a,…] displays in a notebook as a plot of a tree graph with root node containing data a, with children nodes containing data b, c, …:
- Trees can simultaneously express a hierarchy of nodes and store general data in each node, such as XMLElement or Cell expressions.
- In Tree[data,subtrees], the subtrees are other Tree expressions or general expressions that are interpreted as leaves.
- Tree[…] is always converted to a standard form with structure Tree[data,subtrees].
- Tree[subtrees] is equivalent to Tree[Null,subtrees].
- Tree is treated as a raw object by functions like AtomQ.
- A node containing data is represented as Tree[data,subtrees].
- A tree of the form Tree[data,None] is called a leaf. All other trees are of the form Tree[data,{…}] or Tree[data,<|…|>], corresponding to inner nodes with a list or association of children.
- TreeGraph returns a Graph object representing a tree globally as a list of oriented edges between distinct vertices. Tree represents nested subtrees, each containing an independent data expression.
- Options affecting individual tree elements or nodes include:
-
TreeElementLabel labels for subtree elements TreeElementLabelStyle styles for subtree element labels TreeElementLabelFunction generate labels for subtree elements TreeElementStyle styles for subtree elements TreeElementStyleFunction generate styles for subtree elements TreeElementCoordinates coordinates for subtree elements TreeElementSize sizes of subtree elements TreeElementSizeFunction generate sizes of subtree elements TreeElementShape graphic shapes for subtree elements TreeElementShapeFunction generate graphic shapes for subtree elements - Options affecting individual edges include:
-
ParentEdgeLabel labels and label placement for edges ParentEdgeLabelStyle styles for edge labels ParentEdgeLabelFunction generate labels for edges ParentEdgeStyle styles for edges ParentEdgeStyleFunction generate styles for edges ParentEdgeShapeFunction generate graphic shapes for edges - Options affecting elision of nodes include:
-
MaxDisplayedChildren maximum number of children to display - Options affecting the entire tree include:
-
TreeLayout how to lay out subtrees and edges - Tree has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes:
-
FormatType StandardForm the default format type for text FrameTicks None frame ticks MaxDisplayedChildren $MaxDisplayedChildren maximum number of children to display ParentEdgeLabel Automatic labels and label placement for edges ParentEdgeLabelFunction Automatic generate labels for edges ParentEdgeLabelStyle Automatic styles for edge labels ParentEdgeShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for edges ParentEdgeStyle Automatic styles for edges ParentEdgeStyleFunction Automatic generate styles for edges PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize TreeElementCoordinates Automatic coordinates for subtree elements TreeElementLabel Automatic labels for subtree elements TreeElementLabelFunction Automatic generate labels for subtree elements TreeElementLabelStyle Automatic styles for subtree element labels TreeElementShape Automatic graphic shapes for subtree elements TreeElementShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for subtree elements TreeElementSize Automatic sizes of subtree elements TreeElementSizeFunction Automatic generate sizes of subtree elements TreeElementStyle Automatic styles for subtree elements TreeElementStyleFunction Automatic generate styles for subtree elements TreeLayout Automatic how to lay out subtrees and edges
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Scope (4)
Options (11)
Styling Individual Tree Elements (2)
Styling Entire Tree (4)
Tree Layout and Graphics Options (3)
Applications (8)
Create a tree from the hierarchy of tags, attributes and elements:
Convert an XML tree to symbolic XML:
Create a tree from the hierarchy of names and values:
Convert a JSON tree to symbolic JSON:
Create a tree from the hierarchy of subdirectories and files in a directory:
Define a function that converts a TextElement object to a tree:
Define a function that yields the child elements of a TextElement:
Define a function that extracts the "GrammaticalUnit" from a TextElement:
Create a tree from the hierarchy of properties and text:
Convert a text tree to a TextElement:
Get a list of US cities with populations over 100,000:
Construct a graph giving the hierarchical clustering of the cities according to their geodetic positions:
Convert the clustering hierarchy from a Graph object to a Tree object:
For each leaf, obtain the geodetic position of a city from its index in the hierarchical clustering graph:
For each subtree representing a cluster, give the tree containing the spatial median of its children:
Obtain a tree of geodetic positions by using the position of a city for each leaf and the spatial median of the positions for each cluster:
Show the edges in this tree of geodetic positions on a map of the United States:
Create an association giving the dates of birth:
Define a function that compares two people, giving the person who was younger when they had their first child, together with that child and their age when that child was born:
Define a function that compares two siblings, giving the older sibling together with their date of birth, in addition to the youngest first-time parent among their descendants:
Define a function that gives the youngest first-time parent among a person's descendants, given the results for their children:
Find the youngest first-time parent in the tree, together with their first child and their age when the child was born:
Properties & Relations (6)
A node of a tree does not need to have data:
RulesTree returns a Tree expression:
Check whether an expression with head Tree is a valid Tree object:
This is not a valid Tree object:
However, this is a valid Tree object that contains a child with an invalid Tree expression as data:
Construct a Tree expression with ExpressionTree:
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), Tree, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Tree.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "Tree." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Tree.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). Tree. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Tree.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_tree, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Tree}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Tree.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_tree, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Tree}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Tree.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}