ExpressionTree[expr]
gives a Tree object from the structure of the expression expr.
ExpressionTree[expr,struct]
gives a Tree object from the expression expr with data and subtrees as specified by struct.


ExpressionTree
ExpressionTree[expr]
gives a Tree object from the structure of the expression expr.
ExpressionTree[expr,struct]
gives a Tree object from the expression expr with data and subtrees as specified by struct.
Details and Options



- ExpressionTree can construct Tree objects from lists, arrays, rules, XML and arbitrary expressions as specified.
- Possible forms for struct for arbitrary expressions include: »
-
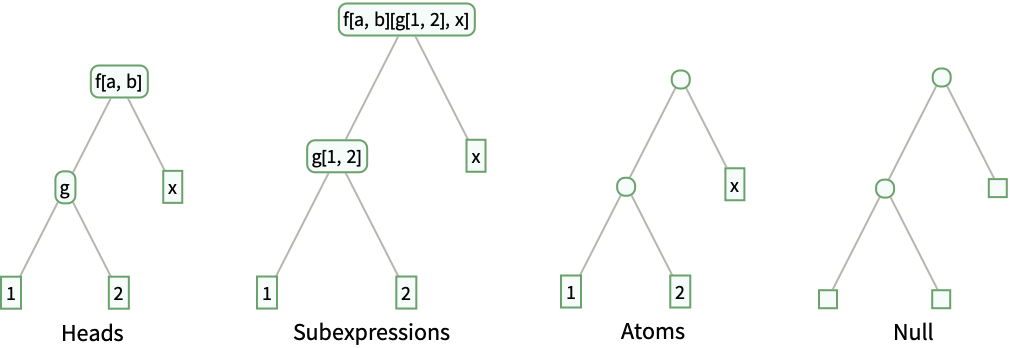
"HeadTrees" trees corresponding to heads of subexpressions of the expression by level "Heads" heads of subexpressions of the expression by level "Subexpressions" subexpressions of the expression by level "Atoms" atomic subexpressions of the expression at level -1 Null subexpressions of the expression by level with no data None the expression itself - ExpressionTree takes the same options as Tree.
- Additional options of ExpressionTree include:
-
Heads include heads of expressions and their parts as subtrees - Possible structures for the expression f[a,b][g[1,2],x] with the default option setting HeadsFalse include:
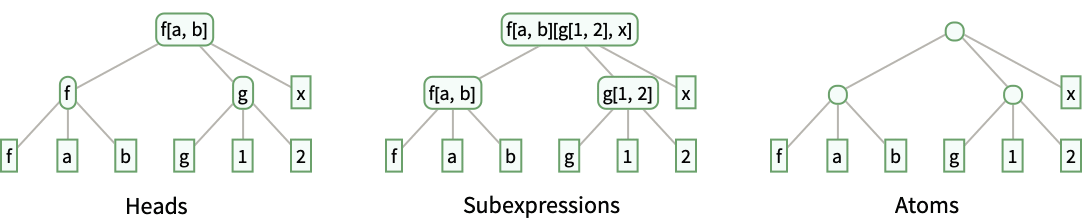
- Versions of these structures with the option setting HeadsTrue include: »
- Held forms for struct for arbitrary expressions include:
-
"HeldHeadTrees" trees corresponding to held heads of subexpressions of the expression by level "HeldHeads" held heads of subexpressions of the expression by level "HeldSubexpressions" held subexpressions of the expression by level "HeldAtoms" held atomic subexpressions of the expression at level -1 - Possible forms for struct for common types of expressions include:
-
"XML" tags, attributes and elements of an XML object - Possible forms for struct for nested lists and associations include: »
-
"List" elements of nested lists "Association" elements of nested associations "Dataset" headers and data of a dataset - Possible forms for struct for nested rules include: »
-
"Rules" left-hand sides and leaves of nested rules "JSON" names and values of a JSON object, using names as data "RawJSON" names and values of a JSON object, using names as keys "FileSystem" directories and files in a file system
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (14)
Arbitrary Expressions (6)
"HeadTrees" (1)
If AtomQ[head] gives True, then ExpressionTree[head[arg1,arg2,…],"HeadTrees"] gives a tree with root containing head and with children given by the ExpressionTree[argi,"HeadTrees"]:
If AtomQ[head] gives False, then ExpressionTree[head[arg1,arg2,…],"HeadTrees"] gives a tree with root containing ExpressionTree[head,"HeadTrees"] rather than head:
ExpressionTree[atom,"HeadTrees"] gives a leaf containing the atomic expression atom:
"Heads" (1)
ExpressionTree[head[arg1,arg2,…],"Heads"] gives a tree with root containing head and with children given by the ExpressionTree[argi,"Heads"]:
ExpressionTree[atom,"Heads"] gives a leaf containing the atomic expression atom:
"Subexpressions" (1)
ExpressionTree[expr0[expr1,expr2,…],"Subexpressions"] gives a tree with root containing expr0[expr1,expr2,…] and with children given by the ExpressionTree[expri,"Subexpressions"]:
ExpressionTree[atom,"Subexpressions"] gives a leaf containing the atomic expression atom:
"Atoms" (1)
ExpressionTree[expr0[expr1,expr2,…],"Atoms"] gives a tree with children given by the ExpressionTree[expri,"Atoms"]:
ExpressionTree[atom,"Atoms"] gives a leaf containing the atomic expression atom:
Null (1)
ExpressionTree[expr0[expr1,expr2,…],Null] gives a tree with children given by the ExpressionTree[expri,Null]:
ExpressionTree[atom,Null] gives a leaf containing Null for an atomic expression atom:
None (1)
ExpressionTree[expr,None] gives a leaf containing expr:
Nested Lists and Associations (3)
Options (11)
Heads (2)
Styling Individual Tree Elements (2)
Styling Entire Tree (4)
Tree Layout and Graphics Options (3)
Properties & Relations (15)
Construct a tree from an expression:
Get back the original expression:
Transform a tree into an expression:
Transform the resulting expression back into a tree:
Construct trees from groupings of a list:
With the default structure "HeadTrees", ExpressionTree constructs a tree with subtrees containing data giving the tree structure of the heads of subexpressions:
The structure "Heads" gives a tree representing the same data as "HeadTrees", but with subtrees containing the heads of subexpressions themselves:
ExpressionTree[expr,"Heads"] gives output similar to TreeForm[expr]:
The structure "Subexpressions" gives a tree with the same shape as the one given by "Heads", but with data containing the subexpressions themselves rather than their heads:
The subtrees of the tree on level n correspond to the parts of the expression on level n, excluding heads:
The structure "Atoms" gives a tree with the same shape as the one given by "Subexpressions", but storing data only in the leaf nodes:
The structure Null gives a tree with the same shape but no data:
Construct a tree from the heads in an expression:
Use TreeFold to insert a parent node above each subtree:
This corresponds to mapping on the arguments in an expression:
Map maps on the arguments in an expression by default:
Construct a tree from the atoms in an expression:
Use TreeFold to insert a sibling node before each subtree:
This corresponds to mapping on the subexpressions in an expression:
Map maps on the subexpressions in an expression with HeadsTrue:
Construct a tree from the heads in an expression:
TreeMap maps on the data of subtrees in a tree:
This corresponds to mapping on the heads and leaves in an expression:
Map can map on the heads and leaves directly:
Construct a tree from the atoms in an expression:
TreeMap can map on the data of just the leaves in a tree:
This corresponds to mapping on the atoms in an expression:
Map can map on the atoms in an expression directly:
Depth[expr] is equivalent to TreeDepth[ExpressionTree[expr]]+1:
Depth[expr,HeadsTrue] is equivalent to TreeDepth[ExpressionTree[expr,"Subexpressions"]]+1:
ExpressionTree evaluates subexpressions before constructing the tree:
Use Unevaluated to defer evaluation of subexpressions until after the tree is constructed:
Held structures ensure that subexpressions are wrapped in HoldForm to prevent all evaluation:
Show the HoldComplete wrappers:
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), ExpressionTree, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ExpressionTree.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "ExpressionTree." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ExpressionTree.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). ExpressionTree. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ExpressionTree.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_expressiontree, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ExpressionTree}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ExpressionTree.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_expressiontree, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ExpressionTree}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ExpressionTree.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}