NestTree[f,tree]
adds children to each leaf of tree, with f[expr] giving the list of data for the new children of a leaf with data expr.
NestTree[f,tree,n]
successively applies f to the data of each leaf up to level n, adding at most n levels to each leaf.
NestTree[f,tree,n,h]
additionally applies h to the data of the new subtrees.
NestTree[f,expr,…]
constructs a tree by nesting f on the tree leaf with data expr.


NestTree
NestTree[f,tree]
adds children to each leaf of tree, with f[expr] giving the list of data for the new children of a leaf with data expr.
NestTree[f,tree,n]
successively applies f to the data of each leaf up to level n, adding at most n levels to each leaf.
NestTree[f,tree,n,h]
additionally applies h to the data of the new subtrees.
NestTree[f,expr,…]
constructs a tree by nesting f on the tree leaf with data expr.
Details and Options

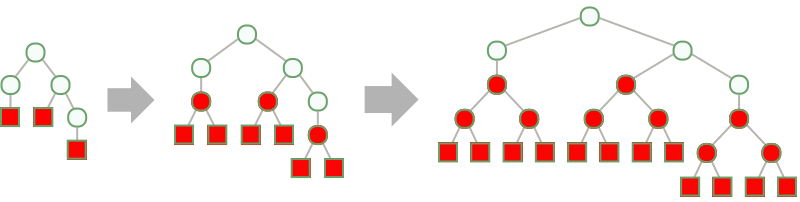
- NestTree grows Tree objects, adding successively deeper levels of children to the leaves using an operation f:
- NestTree is useful for constructing a tree from an expression and extending the leaves of a tree.
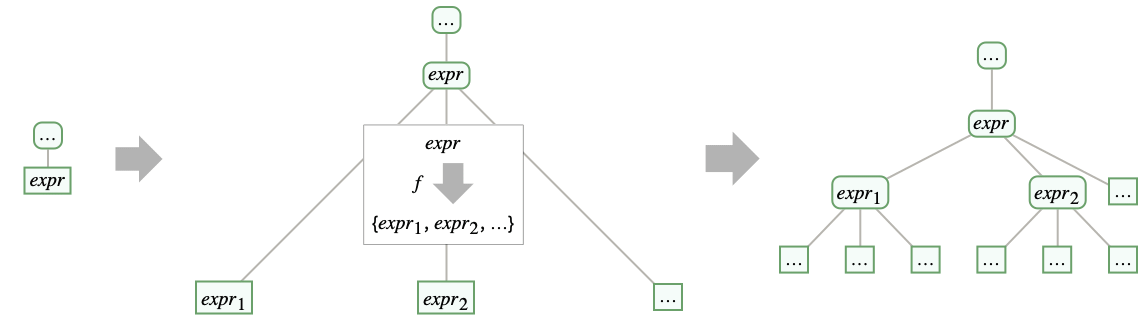
- For each new level of nesting, every leaf Tree[expr,None] is replaced by Tree[expr,{Tree[expr1,None],…}], where f[expr] gives {expr1,expr2,…}: »
- In NestTree[f,tree,n], n can be any non-negative machine integer or Infinity. »
- NestTree[f,tree,n] adds at most n additional levels to each leaf. If f returns None, {}, <||> or Hold[], no further levels are added to that leaf. »
- In NestTree[f,tree,n,h], every leaf Tree[expr,None] is replaced by Tree[h[expr],…], including initial leaves and those generated in intermediate steps. »
- If expr is not an explicit Tree object, then NestTree[f,expr,…] is equivalent to NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None],…]. »
- If f[expr] gives Hold[expr1,expr2,…], then the expressions expri are given to the functions f and h unevaluated in NestTree[f,tree,n,h]. »
- In NestTree[f,tree], f[expr] should give {expr1,expr2,…}, <|key1expr1,key2expr2,…|> Hold[expr1,expr2,…] or None.
- If f does not return {…}, <|…|>, Hold[…] or None, NestTree[f,tree,…] is equivalent to NestTree[List@*f,tree,…]. »
- NestTree[f,tree,0] gives tree. NestTree[f,tree,0,h] is equivalent to TreeMap[h,tree,{-1}].
- If f[expr] gives <|key1expr1,key2expr2,…|>, then NestTree[f,expr,n] gives Tree[expr,<|key1tree1,key2tree2,…|>], where treei is the result of NestTree[f,expri,n-1]. »
- NestTree takes the same options as Tree.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (9)
Options (9)
Styling Individual Tree Elements (2)
Styling Entire Tree (4)
Tree Layout and Graphics Options (3)
Applications (8)
Create a tree from the hierarchy of files in a directory:
Create a tree of terms in a linear recurrence:
Compute the terms of the linear recurrence:
Define a function that converts a TextElement object to a tree:
Define a function that yields the child elements of a TextElement:
Define a function that extracts the "GrammaticalUnit" from a TextElement:
Convert TextElement to a tree:
Properties & Relations (12)
NestList gives a list of the results of successive applications of an operator f to an expression:
NestTree gives a tree of the results of successive applications of an operator f to an expression:
NestTree applies subsequent operators to each element of a list:
NestTree[f,expr,…] constructs a tree starting from the expression expr if expr is not a tree:
This is equivalent to NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None],…]:
If f does not return {…}, <|…|>, Hold[…] or None, NestTree[f,tree,…] is equivalent to NestTree[List@*f,tree,…]:
NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None],0] gives Tree[expr,None]:
NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None]] gives Tree[expr,None] if f[expr] gives None:
NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None]] gives Tree[expr,{…}] if f[expr] gives {…} or Hold[…]:
This is true even if f[expr] gives {} or Hold[]:
NestTree successively applies an operator f until the maximum level is reached or f returns None, {}, <||> or Hold[]:
NestTree[f,Tree[expr,None],n,h] gives the tree with data h[expr] and children NestTree[f,Tree[expri,None],n-1,h], where f[expr] gives {expr1,expr2,…}:
NestTree[TreeChildren,Tree[tree,None],Infinity,TreeData] is equivalent to tree:
NestGraph applies an operator to each vertex in a graph:
NestTree applies an operator to each leaf in a tree:
Imitate the output of CompleteKaryTree using NestTree:
Convert the tree to an actual Graph object:
Generate a tree containing random integers from 0 to 10 and between 1 and 3 children for internal subtrees:
Use RandomTree to generate a random tree of a certain size:
Possible Issues (1)
Neat Examples (3)
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), NestTree, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NestTree.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "NestTree." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NestTree.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). NestTree. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NestTree.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_nesttree, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NestTree}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NestTree.html}", note=[Accessed: 21-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_nesttree, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NestTree}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NestTree.html}, note=[Accessed: 21-February-2026]}