WSOpenArgcArgv (C Function)
-
See Also
- C Functions
- WSActivate()
- WSOpenString()
- Related Guides
- Tech Notes
WSOpenArgcArgv (C Function)
Details
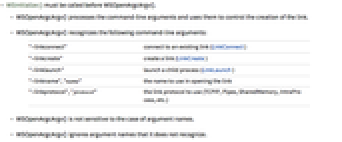
- WSInitialize() must be called before WSOpenArgcArgv().
- WSOpenArgcArgv() processes the command-line arguments and uses them to control the creation of the link.
- WSOpenArgcArgv() recognizes the following command-line arguments:
-
"-linkconnect" connect to an existing link (LinkConnect) "-linkcreate" create a link (LinkCreate) "-linklaunch" launch a child process (LinkLaunch) "-linkname","name" the name to use in opening the link "-linkprotocol","protocol" the link protocol to use (TCPIP, Pipes, SharedMemory, IntraProcess, etc.) - WSOpenArgcArgv() is not sensitive to the case of argument names.
- WSOpenArgcArgv() ignores argument names that it does not recognize.
- WSOpenArgcArgv() is called automatically by the WSMain() function created by wsprep and wscc.
- On some computer systems, giving
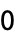 for
for 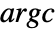 or a null pointer for
or a null pointer for 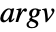 will cause arguments to be requested interactively, typically through a dialog box.
will cause arguments to be requested interactively, typically through a dialog box. - WSOpenArgcArgv() is declared in the WSTP header file wstp.h.
Examples
Basic Examples (1)
#include "wstp.h"
/* create a link using command-line parameters */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
WSENV env;
WSLINK link;
int error;
env = WSInitialize((WSEnvironmentParameter)0);
if(env == (WSENV)0)
{ /* unable to initialize the WSTP environment */ }
/* let WSOpenArgcArgv process the command line */
link = WSOpenArgcArgv(env, argc, argv, &error);
if(link == (WSLINK)0 || error != WSEOK)
{ /* unable to create the link */ }
/* ... */
WSClose(link);
WSDeinitialize(env);
return 0;
}
See Also
C Functions: WSActivate() WSOpenString()
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2007 (6.0)