WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
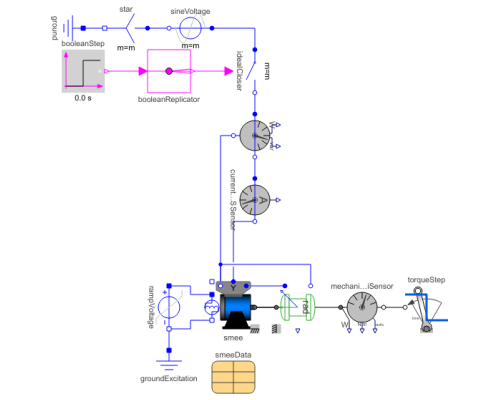
SMEE_DOLTest example: ElectricalExcitedSynchronousMachine starting direct on line |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines.SMEE_DOL"]
Information
This information is part of the Modelica Standard Library maintained by the Modelica Association.
An electrically excited synchronous generator is started direct on line utilizing the damper cage (and the shorted excitation winding) at 0 seconds.
At t = 0.5 seconds, the excitation voltage is raised to achieve the no-load excitation current. Note, that reactive power of the stator goes to zero.
At t = 2 second, a driving torque step is applied to the shaft (i.e. the turbine is activated). Note, that active and reactive power of the stator changes. To drive at higher torque, i.e., produce more electric power, excitation has to be adapted.
Simulate for 3 seconds and plot:
smee.tauElectricalsmee.wMechanicalsmee.ierotorDisplacementAngle.rotorDisplacementAnglecurrentQuasiRMSSensor.IelectricalPowerSensor.PelectricalPowerSensor.QmechanicalMultiSensor.power
Default machine parameters are used.
Note
The mains switch is closed at time = 0 in order to avoid non physical noise calculated by the rotorDisplacementAngle.
This noise is caused by the interaction of the high resistance of the switch and the machine, see
#2388.
Parameters (5)
| VNominal |
Value: 100 Type: Voltage (V) Description: Nominal RMS voltage per phase |
|---|---|
| fNominal |
Value: 50 Type: Frequency (Hz) Description: Nominal frequency |
| Ve |
Value: smeeData.Re * smeeData.IeOpenCircuit Type: Voltage (V) Description: Excitation current |
| gamma0 |
Value: 0 Type: Angle (rad) Description: Initial rotor displacement angle |
| smeeData |
Value: Type: SynchronousMachineData Description: Synchronous machine data |
Components (16)
| smee |
Type: SM_ElectricalExcited Description: Electrical excited synchronous machine with damper cage |
|
|---|---|---|
| rotorDisplacementAngle |
Type: RotorDisplacementAngle Description: Rotor lagging angle |
|
| groundExcitation |
Type: Ground Description: Ground node |
|
| mechanicalMultiSensor |
Type: MultiSensor Description: Ideal sensor to measure the torque and power between two flanges (= flange_a.tau*der(flange_a.phi)) and the absolute angular velocity |
|
| electricalPowerSensor |
Type: ElectricalPowerSensor Description: Instantaneous power from space phasors |
|
| currentQuasiRMSSensor |
Type: CurrentQuasiRMSSensor Description: Length of space phasor -> RMS current |
|
| sineVoltage |
Type: SineVoltage Description: Polyphase sine voltage source |
|
| star |
Type: Star Description: Star-connection |
|
| ground |
Type: Ground Description: Ground node |
|
| rampVoltage |
Type: RampVoltage Description: Ramp voltage source |
|
| terminalBox |
Type: TerminalBox Description: Terminal box Y/D-connection |
|
| smeeData |
Type: SynchronousMachineData Description: Synchronous machine data |
|
| idealCloser |
Type: IdealClosingSwitch Description: Polyphase ideal closer |
|
| booleanStep |
Type: BooleanStep Description: Generate step signal of type Boolean |
|
| booleanReplicator |
Type: BooleanReplicator Description: Boolean signal replicator |
|
| torqueStep |
Type: TorqueStep Description: Constant torque, not dependent on speed |