WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
RotorDisplacementAngleRotor lagging angle |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Sensors.RotorDisplacementAngle"]
Information
This information is part of the Modelica Standard Library maintained by the Modelica Association.
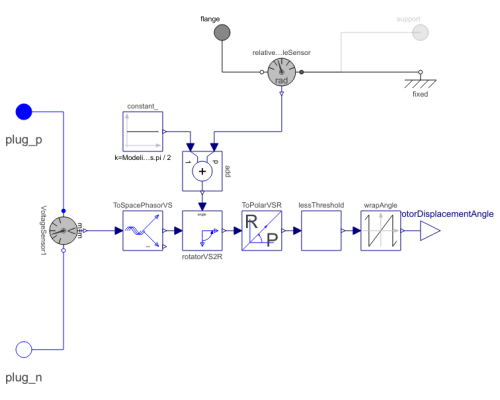
Calculates rotor lagging angle by measuring the stator phase voltages, transforming them to the corresponding space phasor in stator-fixed coordinate system,rotating the space phasor to the rotor-fixed coordinate system and calculating the angle of this space phasor.
The sensor's housing can be implicitly fixed (useSupport=false).
If the machine's stator also implicitly fixed (useSupport=false), the angle at the flange
is equal to the angle of the machine's rotor against the stator.
Otherwise, the sensor's support has to be connected to the machine's support.
Parameters (5)
| m |
Value: 3 Type: Integer Description: Number of phases |
|---|---|
| p |
Value: Type: Integer Description: Number of pole pairs |
| positiveRange |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: Use only positive output range, if true |
| threshold |
Value: 0 Type: Real Description: Below threshold the voltage is considered as zero |
| useSupport |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: Use support or fixed housing |
Connectors (5)
| rotorDisplacementAngle |
Type: RealOutput Description: 'output Real' as connector |
|
|---|---|---|
| plug_p |
Type: PositivePlug Description: Positive polyphase electrical plug with m pins |
|
| plug_n |
Type: NegativePlug Description: Negative polyphase electrical plug with m pins |
|
| flange |
Type: Flange_a Description: One-dimensional rotational flange of a shaft (filled circle icon) |
|
| support |
Type: Flange_a Description: Support at which the reaction torque is acting |
Components (10)
| VoltageSensor1 |
Type: VoltageSensor Description: Polyphase voltage sensor |
|
|---|---|---|
| ToSpacePhasorVS |
Type: ToSpacePhasor Description: Conversion of polyphase instantaneous values to space phasors |
|
| relativeAngleSensor |
Type: RelAngleSensor Description: Ideal sensor to measure the relative angle between two flanges |
|
| constant_ |
Type: Constant Description: Generate constant signal of type Real |
|
| add |
Type: Add Description: Output the sum of the two inputs |
|
| rotatorVS2R |
Type: Rotator Description: Rotates space phasor |
|
| ToPolarVSR |
Type: ToPolar Description: Converts a space phasor to polar coordinates |
|
| fixed |
Type: Fixed Description: Flange fixed in housing at a given angle |
|
| wrapAngle |
Type: WrapAngle Description: Wrap angle to interval ]-pi,pi] or [0,2*pi[ |
|
| lessThreshold |
Type: LessThreshold Description: Sets angle to zero when length is below threshold |
Used in Examples (19)
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: SynchronousMachineReluctanceRotor direct-on-line |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: SynchronousMachineReluctanceRotor with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine fed by current source |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine fed by FOC |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: ElectricalExcitedSynchronousMachine starting direct on line |
|
|
Modelica.Electrical.Machines.Examples.SynchronousMachines Test example: ElectricalExcitedSynchronousMachine as Generator |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines.ComparisonPolyphase Starting of polyphase permanent magnet synchronous machine with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines.ComparisonPolyphase Electrical excited polyphase synchronous machine operating as generator |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines.ComparisonPolyphase Starting of polyphase synchronous reluctance machine with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Starting of permanent magnet synchronous machine with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine fed by current source |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine fed by FOC |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines ElectricalExcitedSynchronousMachine starting direct on line |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Electrical excited synchronous machine operating as generator |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Starting of synchronous reluctance machine with inverter |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.QuasiStatic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Test example: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMachine fed by current source |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.QuasiStatic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Electrical excited synchronous machine operating as generator |
|
|
Modelica.Magnetic.QuasiStatic.FundamentalWave.Examples.BasicMachines.SynchronousMachines Test example: Synchronous reluctance machine fed by current source |
Used in Components (1)
|
Modelica.Blocks.Examples.Noise.Utilities.Parts Synchronous machine with current controller and measurement noise |