NonlinearModelFit[{{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…},form,{β1,…},x]
constructs a nonlinear model with formula form that fits the yi for each xi using the free parameters βi.
NonlinearModelFit[data,form,params,{x1,…}]
constructs a nonlinear model where form depends on the variables xk.
NonlinearModelFit[data,{form,cons},params,{x1,…}]
constructs a nonlinear model subject to the parameter constraints cons.


NonlinearModelFit
NonlinearModelFit[{{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…},form,{β1,…},x]
constructs a nonlinear model with formula form that fits the yi for each xi using the free parameters βi.
NonlinearModelFit[data,form,params,{x1,…}]
constructs a nonlinear model where form depends on the variables xk.
NonlinearModelFit[data,{form,cons},params,{x1,…}]
constructs a nonlinear model subject to the parameter constraints cons.
Details and Options








- NonlinearModelFit attempts to model the input data using a general mathematical formula with free parameters.
- NonlinearModelFit produces a nonlinear model of the form
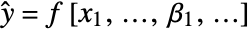 under the assumption that the original
under the assumption that the original 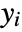 are independent normally distributed with mean
are independent normally distributed with mean 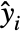 and common standard deviation.
and common standard deviation. - NonlinearModelFit returns a symbolic FittedModel object to represent the nonlinear model it constructs. The properties and diagnostics of the model can be obtained from model["property"].
- The value of the best-fit function from NonlinearModelFit at a particular point x1, … can be found from model[x1,…].
- The best-fit function from NonlinearModelFit[data,form,pars,vars] is the same as the result from FindFit[data,form,pars,vars].
- NonlinearModelFit[data,form,{{β1,val1},…},vars] starts the search for a fit with {β1->val1,…}.
- Possible forms of data are:
-
{y1,y2,…} equivalent to the form {{1,y1},{2,y2},…} {{x11,x12,…,y1},…} a list of independent values xij and the responses yi {{x11,x12,…}y1,…} a list of rules between input values and response {{x11,x12,…},…}{y1,y2,…} a rule between a list of input values and responses {{x11,…,y1,…},…}n fit the n 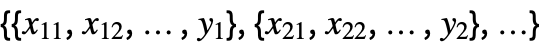 column of a matrix
column of a matrixTabular[…]name fit the column name in a tabular object - With multivariate data such as
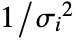 , the number of coordinates xi1, xi2, … should equal the number of variables xi.
, the number of coordinates xi1, xi2, … should equal the number of variables xi. - The data points can be approximate real numbers. Uncertainty can be specified using Around.
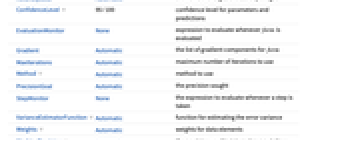
- NonlinearModelFit takes the following options:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic the number of digits of accuracy sought ConfidenceLevel 95/100 confidence level for parameters and predictions EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate whenever form is evaluated Gradient Automatic the list of gradient components for form MaxIterations Automatic maximum number of iterations to use Method Automatic method to use PrecisionGoal Automatic the precision sought StepMonitor None the expression to evaluate whenever a step is taken VarianceEstimatorFunction Automatic function for estimating the error variance Weights Automatic weights for data elements WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations - With ConfidenceLevel->p, probability-p confidence intervals are computed for parameter and prediction intervals.
- With the setting Weights->{w1,w2,…}, the error variance for yi is assumed to be proportional to
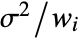 .
. - With the setting Weights->Automatic, the weights will be set to 1 if the data contains exact values. If the data contains Around values, the weights will be set to
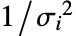 , with
, with 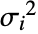 the total response variance.
the total response variance. - The total response variance
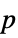 is a function of the initial response variance Δyi2 and the independent values variance
is a function of the initial response variance Δyi2 and the independent values variance 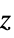 .
. - The uncertainties
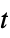 are propagated through the model using AroundReplace, and the resulting variance is added to response variance Δyi2. The function FindRoot is used internally to find a self-consistent solution according to the Fasano and Vio method.
are propagated through the model using AroundReplace, and the resulting variance is added to response variance Δyi2. The function FindRoot is used internally to find a self-consistent solution according to the Fasano and Vio method. - With the setting VarianceEstimatorFunction->f, the common variance is estimated by f[res,w], where res={y1-
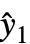 ,y2-
,y2-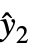 ,…} is the list of residuals and w is the list of weights.
,…} is the list of residuals and w is the list of weights. - Using VarianceEstimatorFunction->(1&) and Weights->{1/Δy12,1/Δy22,…}, Δyi is treated as the known uncertainty of measurement yi, and parameter standard errors are effectively computed only from the weights.
- Possible settings for Method include:
-
"ConjugateGradient" nonlinear conjugate gradient "Gradient" gradient descent "LevenbergMarquardt" Gauss–Newton method for least squares "Newton" Newton method "QuasiNewton" quasi-Newton BFGS "InteriorPoint" interior point method "NMinimize" use NMinimize for optimization Automatic automatic default method - Additional method suboptions can be given in the form Method->{…,opts}.
- The Method option can take any local optimization method as specified in the tutorial Unconstrained Optimization: Methods for Local Minimization. »
- Any global optimization method can be specified as a submethod to the "NMinimize" method. They can be found in the Numerical Algorithms for Constrained Global Optimization tutorial. »
- For constrained models, properties based on approximate normality assumptions may not be valid. When such values are computed, the values are generated along with a warning message.
- Properties related to data and the fitted function using model["property"] include:
-
"BestFit" fitted function "BestFitAround" fitted function and mean uncertainty "BestFitDataAround" fitted function and data uncertainty "BestFitParameters" parameter estimates "Data" the input data or design matrix and response vector "Function" best-fit pure function "Response" response values in the input data "Weights" weights used to fit the data - Types of residuals include:
-
"FitResiduals" difference between actual and predicted responses "StandardizedResiduals" fit residuals divided by the standard error for each residual "StudentizedResiduals" fit residuals divided by single deletion error estimates - Properties related to the sum of squared errors include:
-
"ANOVA" analysis of variance data "EstimatedVariance" estimate of the error variance - Properties and diagnostics for parameter estimates include:
-
"CorrelationMatrix" asymptotic parameter correlation matrix "CovarianceMatrix" asymptotic parameter covariance matrix "ParameterEstimates" table of fitted parameter information "ParameterBias" estimated bias in the parameter estimates "ParameterConfidenceRegion" ellipsoidal parameter confidence region - Properties for curvature diagnostics include:
-
"CurvatureConfidenceRegion" confidence region for curvature diagnostics "FitCurvature" table of fit curvature information "MaxIntrinsicCurvature" measure of maximum intrinsic curvature "MaxParameterEffectsCurvature" measure of maximum parameter effects curvature - Properties related to influence measures include:
-
"HatDiagonal" diagonal elements of the hat matrix "SingleDeletionVariances" list of variance estimates with the 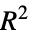
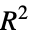 data point omitted
data point omitted - Properties of predicted values include:
-
"MeanPredictionBands" confidence bands for mean predictions "MeanPredictions" data about mean predictions "PredictedResponse" fitted values for the data "SinglePredictionBands" confidence bands based on single observations "SinglePredictions" data about the predicted response of single observations - Properties that measure goodness of fit include:
-
"AdjustedRSquared" 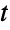 adjusted for the number of model parameters
adjusted for the number of model parameters"AIC" Akaike Information Criterion "AICc" finite sample corrected AIC "BIC" Bayesian Information Criterion "RSquared" coefficient of determination 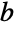
- The properties "BestFit", "BestFitAround", "BestFitDataAround", "SinglePredictionBands" and "MeanPredictionBands" can also be called as {"prop",x} or {"prop",{x1,x2,…}} to evaluate these properties at specific independent values.
Data
Options
Properties
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (15)
Data (7)
Fit a model of one variable, assuming increasing integer-independent values:
Fit a model of more than one variable:
Fit a rule of input values and responses:
Specify a column as the response:
Give starting values when parameters are far from the default value 1:
With the default starting values, the model is effectively 0:
Obtain a list of available properties for a nonlinear model:
Properties (8)
Data & Fitted Functions (1)
Residuals (1)
Sums of Squares (1)
Parameter Estimation Diagnostics (1)
Curvature Diagnostics (1)
Influence Measures (1)
Prediction Values (1)
Generalizations & Extensions (2)
Fit data to a model defined by a numerical operation:
Use ParametricNDSolveValue to make the computation much faster by caching solutions of the differential equation:
Perform other mathematical operations on the functional form of the model:
Integrate symbolically and numerically:
Find a predictor value that gives a particular value for the model:
Options (10)
ConfidenceLevel (1)
The default gives 95% confidence intervals:
Set the level to 90% within FittedModel:
Method (3)
Use the default method for minimizing the least-squares objective function:
Use Newton's method for optimization:
Configure the step control method for Newton's algorithm:
Use the interior point method with constraints:
Perform a more exhaustive search with the global optimization methods from NMinimize:
Use the submethod "RandomSearch":
Specify the number of initial search points for the "RandomSearch" algorithm:
VarianceEstimatorFunction (1)
Weights (4)
Fit a model using equal weights:
Give explicit weights for the data points:
Use Around values to give different weights to data points:
Find the weights that were used to account for the uncertainty in the data:
Use Around values in both the independent values and responses:
In some cases, the root finding algorithm that handles uncertainty in the independent variates does not converge using the standard option settings:
Use the FixedPoint algorithm with a low DampingFactor and high MaxIterations to reach convergence:
WorkingPrecision (1)
Use WorkingPrecision to get higher precision in parameter estimates:
Reduce the precision in property computations after the fitting:
Applications (1)
Properties & Relations (6)
NonlinearModelFit fits linear and nonlinear models assuming normally distributed errors:
LinearModelFit fits linear models assuming normally distributed errors:
FindFit and NonlinearModelFit fit equivalent models:
NonlinearModelFit allows for extraction of additional information about the fitting:
NonlinearModelFit assumes normally distributed responses:
LogitModelFit assumes binomially distributed responses:
The same is true for ProbitModelFit:
NonlinearModelFit will use the time stamps of a TimeSeries as variables:
Rescale the time stamps and fit again:
NonlinearModelFit acts pathwise on a multipath TemporalData:
Compute the AIC from first principles:
Possible Issues (3)
Distributional assumptions are based upon an unconstrained model:
Here the confidence interval for ![]() contains points that violate the constraint:
contains points that violate the constraint:
The coefficient of determination ![]() in NonlinearModelFit is calculated with uncorrected data:
in NonlinearModelFit is calculated with uncorrected data:
The coefficient of determination:
Direct calculation using residuals and data:
Sometimes ![]() is defined using centralized data:
is defined using centralized data:
Fit data that spans over multiple orders of magnitude:
An exponential fit might appear correct at first glance:
But shows significant deviations on a log scale:
This can be addressed by using weights inversely proportional to the variance:
See Also
LinearModelFit GeneralizedLinearModelFit FittedModel FindFit Fit TimeSeriesModelFit FindFormula FindMinimum NMinimize
Function Repository: MultiNonlinearModelFit
History
Introduced in 2008 (7.0) | Updated in 2023 (13.3) ▪ 2024 (14.1) ▪ 2025 (14.2) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), NonlinearModelFit, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearModelFit.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "NonlinearModelFit." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearModelFit.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). NonlinearModelFit. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearModelFit.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_nonlinearmodelfit, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NonlinearModelFit}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearModelFit.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_nonlinearmodelfit, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NonlinearModelFit}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearModelFit.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-February-2026]}