is ![]() , with numerical value
, with numerical value ![]() .
.


Pi 
is ![]() , with numerical value
, with numerical value ![]() .
.
Details
- Mathematical constant treated as numeric by NumericQ and as a constant by D.
- Pi can be evaluated to any numerical precision using N.
- Pi can be entered in StandardForm and InputForm as π,
 pi
pi ,
,  p
p or \[Pi].
or \[Pi]. - In StandardForm, Pi is printed as π.
Background & Context
- Pi is the symbol representing the mathematical constant
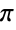 , which can also be input as ∖[Pi]. Pi is defined as the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter and has numerical value
, which can also be input as ∖[Pi]. Pi is defined as the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter and has numerical value 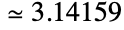 . Pi arises in many mathematical computations including trigonometric expressions, special function values, sums, products, and integrals as well as in formulas from a wide range of mathematical and scientific fields.
. Pi arises in many mathematical computations including trigonometric expressions, special function values, sums, products, and integrals as well as in formulas from a wide range of mathematical and scientific fields. - When Pi is used as a symbol, it is propagated as an exact quantity. While many expressions involving Pi (e.g. Cos[Pi/10]) are automatically expanded in terms of simpler functions, expansion and simplification of more complicated expressions involving Pi (e.g. Cos[Pi/15]) may require use of functions such as FunctionExpand and FullSimplify.
- Pi is known to be both irrational and transcendental, meaning it can be expressed neither as a ratio of integers nor as the root of any integer polynomial. While it is not known if Pi is normal (meaning the digits in its base-
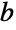 expansion are equally distributed) to any base, its known digits are very uniformly distributed.
expansion are equally distributed) to any base, its known digits are very uniformly distributed. - Pi can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision by means of the Chudnovsky formula using N. In fact, calculating the first million decimal digits of Pi takes only a fraction of a second on a modern desktop computer. RealDigits can be used to return a list of digits of Pi and ContinuedFraction to obtain terms of its continued fraction expansion.
- Most angle-related functions in the Wolfram Language take radian measures as their arguments and return radian measures as results. The symbol Degree, which is equal to Pi/180, can therefore be used as a multiplier when entering values in degree measures (e.g. Cos[30 Degree]).
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Applications (5)
Properties & Relations (2)
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 1996 (3.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Pi, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Pi.html (updated 1996).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Pi." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 1996. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Pi.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Pi. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Pi.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_pi, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Pi}", year="1996", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Pi.html}", note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_pi, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Pi}, year={1996}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Pi.html}, note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}